Page 541 - Design of Reinforced Masonry Structures
P. 541
SHEAR WALLS 7.103
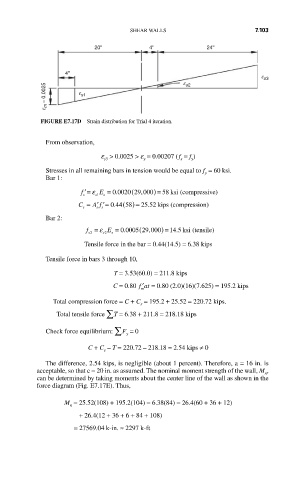
20'' 4'' 24''
4''
e s3
e m = 0.0025 e s1
e s2
FIGURE E7.17D Strain distribution for Trial 4 iteration.
From observation,
e > 0.0025 > e = 0.00207 ( f = f )
s3
y
s
y
Stresses in all remaining bars in tension would be equal to f = 60 ksi.
y
Bar 1:
f s ′= ε s1 E s = 0 0020. (29 000 ) = 58 ksi (compressive)
,
8
A f
.
5
C = ′′= 044. ( ) = 2552 kips (compression)
s
s s
Bar 2:
(
f = ε s2 E = 0 0005 29 000) = 14 5 ksi (tensile)
,
.
.
s2
s
Tensile force in the bar = 0.44(14.5) = 6.38 kips
Tensile force in bars 3 through 10,
T = 3.53(60.0) = 211.8 kips
C = 0.80 ′ fat = 0.80 (2.0)(16)(7.625) = 195.2 kips
m
Total compression force = C + C = 195.2 + 25.52 = 220.72 kips.
s
Total tensile force ∑ T = 6.38 + 211.8 = 218.18 kips
Check force equilibrium: ∑ F = 0
y
C + C – T = 220.72 – 218.18 = 2.54 kips ≠ 0
s
The difference, 2.54 kips, is negligible (about 1 percent). Therefore, a = 16 in. is
acceptable, so that c = 20 in. as assumed. The nominal moment strength of the wall, M ,
n
can be determined by taking moments about the center line of the wall as shown in the
force diagram (Fig. E7.17E). Thus,
M = 25.52(108) + 195.2(104) − 6.38(84) − 26.4(60 + 36 + 12)
n
+ 26.4(12 + 36 + 6 + 84 + 108)
= 27569.04 k-in. ≈ 2297 k-ft