Page 119 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 119
104 Chapter 4 Process Synthesis and Design Optimization
. For separation of low concentration (<1%) components, evaluate distillation
versus selective absorption/stripping/adsorption/chemisorption. Examples
include drying of hydrocarbon streams, removal of color or deactivating com-
ponents, and removal of CO 2 and H 2 S.
. Breaking of azeotropes requires evaluation of the following generic tech-
niques:
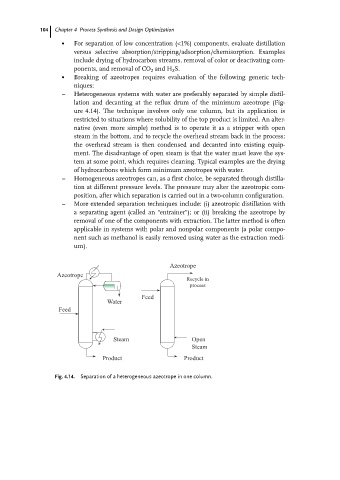
± Heterogeneous systems with water are preferably separated by simple distil-
lation and decanting at the reflux drum of the minimum azeotrope (Fig-
ure 4.14). The technique involves only one column, but its application is
restricted to situations where solubility of the top product is limited. An alter-
native (even more simple) method is to operate it as a stripper with open
steam in the bottom, and to recycle the overhead stream back in the process;
the overhead stream is then condensed and decanted into existing equip-
ment. The disadvantage of open steam is that the water must leave the sys-
tem at some point, which requires cleaning. Typical examples are the drying
of hydrocarbons which form minimum azeotropes with water.
± Homogeneous azeotropes can, as a first choice, be separated through distilla-
tion at different pressure levels. The pressure may alter the azeotropic com-
position, after which separation is carried out in a two-column configuration.
± More extended separation techniques include: (i) azeotropic distillation with
a separating agent (called an ªentrainerº); or (ii) breaking the azeotrope by
removal of one of the components with extraction. The latter method is often
applicable in systems with polar and nonpolar components (a polar compo-
nent such as methanol is easily removed using water as the extraction medi-
um).
Azeotrope
Azeotrope
Recycle in
process
Feed
Water
Feed
Steam Open
Steam
Product Product
Fig. 4.14. Separation of a heterogeneous azeotrope in one column.