Page 196 - Design of Simple and Robust Process Plants
P. 196
5.6 Overall Process Simplification 181
when the feed contains heavies to be separated, the conversion is incomplete, and
the products formed are lighter than the feed (see Figure 5.13).
A generic rule is that a feed to a reactor system can be distilled coupled with a
reactor outlet stream if:
. the reactor conversion is incomplete;
. the boiling points of heavies and light at a selected pressure level can be
handled with practical utility conditions;
. the feed (reactant) contains lights and the reactor outlet stream or its purified
stream contains heavier products compared with the feed (see Figure 5.12);
and
. the feed contains heavier, and the reactor outlet stream or its purified stream
contains lighter, products for separation (see Figure 5.13).
The evolution of the separation train as shown in Figures 4.16±4.20 in Chapter 4 is
an ultimate example of the combination of separations.
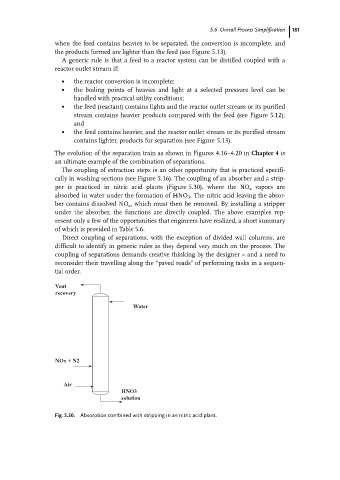
The coupling of extraction steps is an other opportunity that is practiced specifi-
cally in washing sections (see Figure 5.16). The coupling of an absorber and a strip-
per is practiced in nitric acid plants (Figure 5.30), where the NO x vapors are
absorbed in water under the formation of HNO 3 . The nitric acid leaving the absor-
ber contains dissolved NO x , which must then be removed. By installing a stripper
under the absorber, the functions are directly coupled. The above examples rep-
resent only a few of the opportunities that engineers have realized, a short summary
of which is provided in Table 5.6.
Direct coupling of separations, with the exception of divided wall columns, are
difficult to identify in generic rules as they depend very much on the process. The
coupling of separations demands creative thinking by the designer ± and a need to
reconsider their travelling along the ªpaved roadsº of performing tasks in a sequen-
tial order.
Vent
recovery
Water
NOx+N2
Air
HNO3
solution
Fig. 5.30. Absorption combined with stripping in an nitric acid plant.