Page 267 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 267
Image Enhancement 229
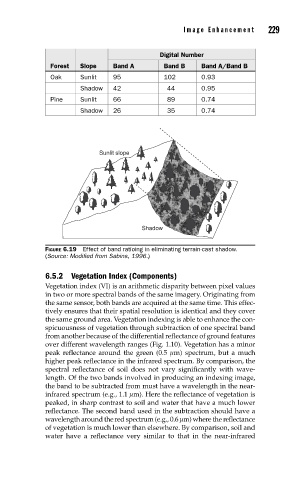
Digital Number
Forest Slope Band A Band B Band A/Band B
Oak Sunlit 95 102 0.93
Shadow 42 44 0.95
Pine Sunlit 66 89 0.74
Shadow 26 35 0.74
Sunlit slope
Shadow
FIGURE 6.19 Effect of band ratioing in eliminating terrain-cast shadow.
(Source: Modifi ed from Sabins, 1996.)
6.5.2 Vegetation Index (Components)
Vegetation index (VI) is an arithmetic disparity between pixel values
in two or more spectral bands of the same imagery. Originating from
the same sensor, both bands are acquired at the same time. This effec-
tively ensures that their spatial resolution is identical and they cover
the same ground area. Vegetation indexing is able to enhance the con-
spicuousness of vegetation through subtraction of one spectral band
from another because of the differential reflectance of ground features
over different wavelength ranges (Fig. 1.10). Vegetation has a minor
peak reflectance around the green (0.5 μm) spectrum, but a much
higher peak reflectance in the infrared spectrum. By comparison, the
spectral reflectance of soil does not vary significantly with wave-
length. Of the two bands involved in producing an indexing image,
the band to be subtracted from must have a wavelength in the near-
infrared spectrum (e.g., 1.1 μm). Here the reflectance of vegetation is
peaked, in sharp contrast to soil and water that have a much lower
reflectance. The second band used in the subtraction should have a
wavelength around the red spectrum (e.g., 0.6 μm) where the reflectance
of vegetation is much lower than elsewhere. By comparison, soil and
water have a reflectance very similar to that in the near-infrared