Page 271 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 271
Image Enhancement 233
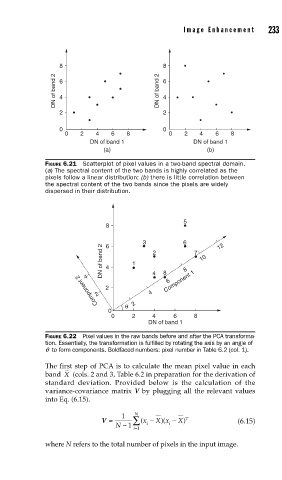
8 2 8
DN of band 2 6 4 DN of band 6 4
2 2
0 0
0 2 4 6 8 0 2 4 6 8
DN of band 1 DN of band 1
(a) (b)
FIGURE 6.21 Scatterplot of pixel values in a two-band spectral domain.
(a) The spectral content of the two bands is highly correlated as the
pixels follow a linear distribution; (b) there is little correlation between
the spectral content of the two bands since the pixels are widely
dispersed in their distribution.
5
8
3 6 12
6
DN of band 2 4 1 2 7 10
8
4 4 8 Component 1
Component 2 2
6
2 4
θ 2
0
0 2 4 6 8
DN of band 1
FIGURE 6.22 Pixel values in the raw bands before and after the PCA transforma-
tion. Essentially, the transformation is fulfi lled by rotating the axis by an angle of
q to form components. Boldfaced numbers: pixel number in Table 6.2 (col. 1).
The first step of PCA is to calculate the mean pixel value in each
band X (cols. 2 and 3, Table 6.2 in preparation for the derivation of
standard deviation. Provided below is the calculation of the
variance-covariance matrix V by plugging all the relevant values
into Eq. (6.15).
N
V = 1 ∑ x ( − X x − X) T (6.15)
(
)
N − 1 i i
i =1
where N refers to the total number of pixels in the input image.