Page 53 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 53
26 Cha pte r T w o
analog materials into the digital format. Finally, this chapter concentrates
on the proper selection of remotely sensed data for a given application.
2.1 Meteorological Satellite Data
Among all remote sensing satellites, meteorological satellites have the
longest history. Of the existing meteorological satellite data, the most
widely known and used are from the AVHRR sensors aboard the
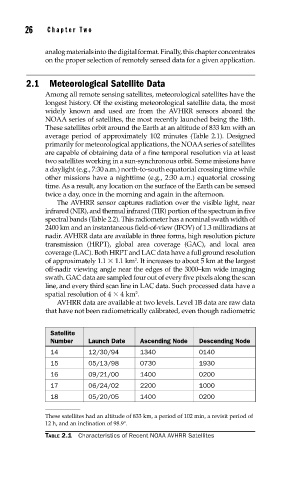
NOAA series of satellites, the most recently launched being the 18th.
These satellites orbit around the Earth at an altitude of 833 km with an
average period of approximately 102 minutes (Table 2.1). Designed
primarily for meteorological applications, the NOAA series of satellites
are capable of obtaining data of a fine temporal resolution via at least
two satellites working in a sun-synchronous orbit. Some missions have
a daylight (e.g., 7:30 a.m.) north-to-south equatorial crossing time while
other missions have a nighttime (e.g., 2:30 a.m.) equatorial crossing
time. As a result, any location on the surface of the Earth can be sensed
twice a day, once in the morning and again in the afternoon.
The AVHRR sensor captures radiation over the visible light, near
infrared (NIR), and thermal infrared (TIR) portion of the spectrum in five
spectral bands (Table 2.2). This radiometer has a nominal swath width of
2400 km and an instantaneous field-of-view (IFOV) of 1.3 milliradians at
nadir. AVHRR data are available in three forms, high resolution picture
transmission (HRPT), global area coverage (GAC), and local area
coverage (LAC). Both HRPT and LAC data have a full ground resolution
2
of approximately 1.1 1.1 km . It increases to about 5 km at the largest
off-nadir viewing angle near the edges of the 3000–km wide imaging
swath. GAC data are sampled four out of every five pixels along the scan
line, and every third scan line in LAC data. Such processed data have a
2
spatial resolution of 4 4 km .
AVHRR data are available at two levels. Level 1B data are raw data
that have not been radiometrically calibrated, even though radiometric
Satellite
Number Launch Date Ascending Node Descending Node
14 12/30/94 1340 0140
15 05/13/98 0730 1930
16 09/21/00 1400 0200
17 06/24/02 2200 1000
18 05/20/05 1400 0200
These satellites had an altitude of 833 km, a period of 102 min, a revisit period of
12 h, and an inclination of 98.9°.
TABLE 2.1 Characteristics of Recent NOAA AVHRR Satellites