Page 58 - Digital Analysis of Remotely Sensed Imagery
P. 58
Overview of Remotely Sensed Data 31
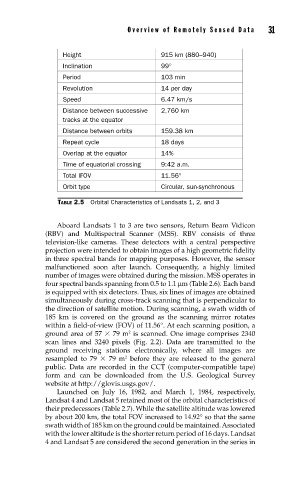
Height 915 km (880–940)
Inclination 99°
Period 103 min
Revolution 14 per day
Speed 6.47 km/s
Distance between successive 2,760 km
tracks at the equator
Distance between orbits 159.38 km
Repeat cycle 18 days
Overlap at the equator 14%
Time of equatorial crossing 9:42 a.m.
Total IFOV 11.56°
Orbit type Circular, sun-synchronous
TABLE 2.5 Orbital Characteristics of Landsats 1, 2, and 3
Aboard Landsats 1 to 3 are two sensors, Return Beam Vidicon
(RBV) and Multispectral Scanner (MSS). RBV consists of three
television-like cameras. These detectors with a central perspective
projection were intended to obtain images of a high geometric fidelity
in three spectral bands for mapping purposes. However, the sensor
malfunctioned soon after launch. Consequently, a highly limited
number of images were obtained during the mission. MSS operates in
four spectral bands spanning from 0.5 to 1.1 μm (Table 2.6). Each band
is equipped with six detectors. Thus, six lines of images are obtained
simultaneously during cross-track scanning that is perpendicular to
the direction of satellite motion. During scanning, a swath width of
185 km is covered on the ground as the scanning mirror rotates
within a field-of-view (FOV) of 11.56°. At each scanning position, a
2
ground area of 57 79 m is scanned. One image comprises 2340
scan lines and 3240 pixels (Fig. 2.2). Data are transmitted to the
ground receiving stations electronically, where all images are
2
resampled to 79 79 m before they are released to the general
public. Data are recorded in the CCT (computer-compatible tape)
form and can be downloaded from the U.S. Geological Survey
website at http://glovis.usgs.gov/.
Launched on July 16, 1982, and March 1, 1984, respectively,
Landsat 4 and Landsat 5 retained most of the orbital characteristics of
their predecessors (Table 2.7). While the satellite altitude was lowered
by about 200 km, the total FOV increased to 14.92° so that the same
swath width of 185 km on the ground could be maintained. Associated
with the lower altitude is the shorter return period of 16 days. Landsat
4 and Landsat 5 are considered the second generation in the series in