Page 108 - Distributed model predictive control for plant-wide systems
P. 108
82 Distributed Model Predictive Control for Plant-Wide Systems
1
0.5
y 1
0
−0.5
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Time (s)
1
0.5
y 2
0
−0.5
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Time (s)
0.5
u 1
0
−0.5
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Time (s)
2
1
u 2
0
−1
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40
Time (s)
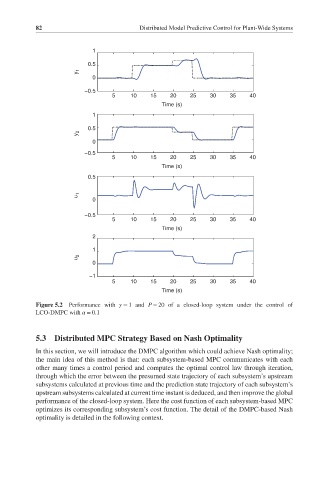
Figure 5.2 Performance with = 1and P = 20 of a closed-loop system under the control of
LCO-DMPC with = 0.1
5.3 Distributed MPC Strategy Based on Nash Optimality
In this section, we will introduce the DMPC algorithm which could achieve Nash optimality;
the main idea of this method is that: each subsystem-based MPC communicates with each
other many times a control period and computes the optimal control law through iteration,
through which the error between the presumed state trajectory of each subsystem’s upstream
subsystems calculated at previous time and the prediction state trajectory of each subsystem’s
upstream subsystems calculated at current time instant is deduced, and then improve the global
performance of the closed-loop system. Here the cost function of each subsystem-based MPC
optimizes its corresponding subsystem’s cost function. The detail of the DMPC-based Nash
optimality is detailed in the following context.