Page 67 - Distributed model predictive control for plant-wide systems
P. 67
Control Structure of Distributed MPC 41
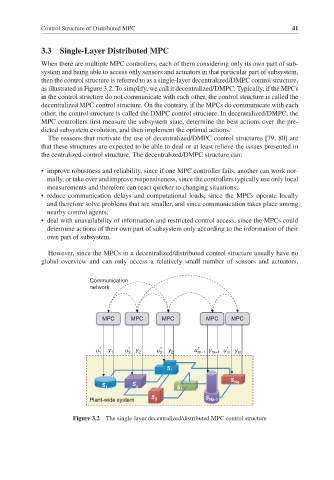
3.3 Single-Layer Distributed MPC
When there are multiple MPC controllers, each of them considering only its own part of sub-
system and being able to access only sensors and actuators in that particular part of subsystem,
then the control structure is referred to as a single-layer decentralized/DMPC control structure,
as illustrated in Figure 3.2. To simplify, we call it decentralized/DMPC. Typically, if the MPCs
in the control structure do not communicate with each other, the control structure is called the
decentralized MPC control structure. On the contrary, if the MPCs do communicate with each
other, the control structure is called the DMPC control structure. In decentralized/DMPC, the
MPC controllers first measure the subsystem state, determine the best actions over the pre-
dicted subsystem evolution, and then implement the optimal actions.
The reasons that motivate the use of decentralized/DMPC control structures [79, 80] are
that these structures are expected to be able to deal or at least relieve the issues presented in
the centralized control structure. The decentralized/DMPC structure can:
• improve robustness and reliability, since if one MPC controller fails, another can work nor-
mally, or take over and improve responsiveness, since the controllers typically use only local
measurements and therefore can react quicker to changing situations;
• reduce communication delays and computational loads, since the MPCs operate locally
and therefore solve problems that are smaller, and since communication takes place among
nearby control agents;
• deal with unavailability of information and restricted control access, since the MPCs could
determine actions of their own part of subsystem only according to the information of their
own part of subsystem.
However, since the MPCs in a decentralized/distributed control structure usually have no
global overview and can only access a relatively small number of sensors and actuators,
Communication
network
MPC MPC MPC MPC MPC
u * 1 y 1 u * 2 y 2 u * 2 y 2 u * m–1 y m–1 u * m y m
S *
S Na
S 1 S 2 S *
S S
Plant-wide system 3 Na-1
Figure 3.2 The single-layer decentralized/distributed MPC control structure