Page 70 - Distributed model predictive control for plant-wide systems
P. 70
44 Distributed Model Predictive Control for Plant-Wide Systems
Supervisory MPC
MPC for reactor MPC for fractionation
LE
HVGO
HPS
LN
Fired
Heater Hydrotreater Hydrocracker Hydrocracker LPS Fractionation HN
Kerosene
Hydrogen
Up
Make up Diesel
Bottom
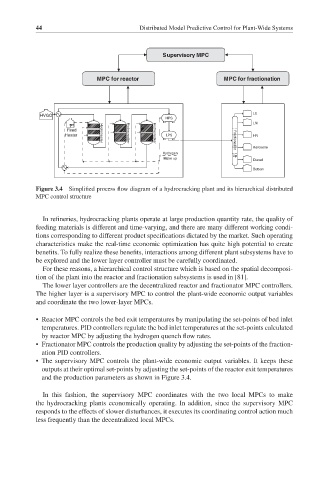
Figure 3.4 Simplified process flow diagram of a hydrocracking plant and its hierarchical distributed
MPC control structure
In refineries, hydrocracking plants operate at large production quantity rate, the quality of
feeding materials is different and time-varying, and there are many different working condi-
tions corresponding to different product specifications dictated by the market. Such operating
characteristics make the real-time economic optimization has quite high potential to create
benefits. To fully realize these benefits, interactions among different plant subsystems have to
be explored and the lower layer controller must be carefully coordinated.
For these reasons, a hierarchical control structure which is based on the spatial decomposi-
tion of the plant into the reactor and fractionation subsystems is used in [81].
The lower layer controllers are the decentralized reactor and fractionator MPC controllers.
The higher layer is a supervisory MPC to control the plant-wide economic output variables
and coordinate the two lower-layer MPCs.
• Reactor MPC controls the bed exit temperatures by manipulating the set-points of bed inlet
temperatures. PID controllers regulate the bed inlet temperatures at the set-points calculated
by reactor MPC by adjusting the hydrogen quench flow rates.
• Fractionator MPC controls the production quality by adjusting the set-points of the fraction-
ation PID controllers.
• The supervisory MPC controls the plant-wide economic output variables. It keeps these
outputs at their optimal set-points by adjusting the set-points of the reactor exit temperatures
and the production parameters as shown in Figure 3.4.
In this fashion, the supervisory MPC coordinates with the two local MPCs to make
the hydrocracking plants economically operating. In addition, since the supervisory MPC
responds to the effects of slower disturbances, it executes its coordinating control action much
less frequently than the decentralized local MPCs.