Page 77 - Distributed model predictive control for plant-wide systems
P. 77
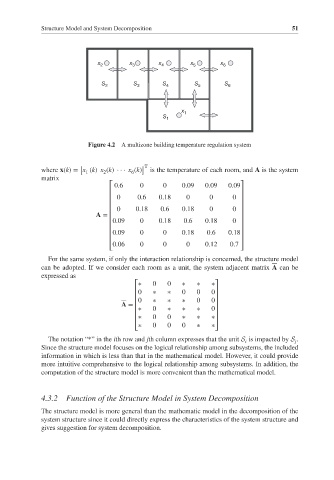
Structure Model and System Decomposition 51
x 2 x 3 x 4 x 5 x 6
S 2 S 3 S 4 S 5 S 6
x 1
S 1
Figure 4.2 A multizone building temperature regulation system
[ ] T
where x(k)= x (k) x (k) ··· x (k) is the temperature of each room, and A is the system
1
6
2
matrix
⎡ 0.6 0 0 0.09 0.09 0.09⎤
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 0 0.6 0.18 0 0 0 ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 0 0.18 0.6 0.18 0 0 ⎥
A =
⎢ ⎥
0.09 0 0.18 0.6 0.18 0
⎢ ⎥
⎢ ⎥
0.09 0 0 0.18 0.6 0.18
⎢ ⎥
⎢ 0.06 0 0 0 0.12 0.7 ⎥
⎣ ⎦
For the same system, if only the interaction relationship is concerned, the structure model
can be adopted. If we consider each room as a unit, the system adjacent matrix A can be
expressed as
⎡∗ 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗⎤
⎢ 0 ∗ ∗ 0 0 0 ⎥
⎢ 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0 0 ⎥
A = ⎢ ⎥
⎢∗ 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ 0⎥
⎢ ∗ 0 0 ∗ ∗ ∗ ⎥
⎢ ⎥
⎣ ∗ 0 0 0 ∗ ∗ ⎦
The notation “*” in the ith row and jth column expresses that the unit S is impacted by S .
i j
Since the structure model focuses on the logical relationship among subsystems, the included
information in which is less than that in the mathematical model. However, it could provide
more intuitive comprehensive to the logical relationship among subsystems. In addition, the
computation of the structure model is more convenient than the mathematical model.
4.3.2 Function of the Structure Model in System Decomposition
The structure model is more general than the mathematic model in the decomposition of the
system structure since it could directly express the characteristics of the system structure and
gives suggestion for system decomposition.