Page 275 - Drilling Technology in Nontechnical Language
P. 275
266 Drilling Technology in Nontechnical Language Second Edition
Subsea BOP systems
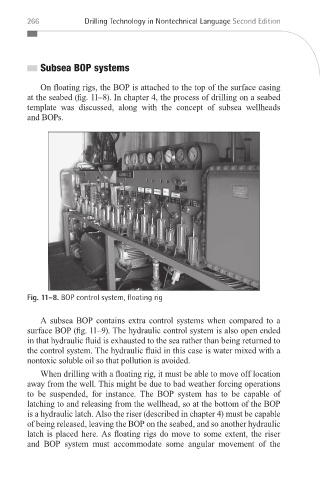
On floating rigs, the BOP is attached to the top of the surface casing
at the seabed (fig. 11–8). In chapter 4, the process of drilling on a seabed
template was discussed, along with the concept of subsea wellheads
and BOPs.
Fig. 11–8. BOP control system, oating rig
A subsea BOP contains extra control systems when compared to a
surface BOP (fig. 11–9). The hydraulic control system is also open ended
in that hydraulic fluid is exhausted to the sea rather than being returned to
the control system. The hydraulic fluid in this case is water mixed with a
nontoxic soluble oil so that pollution is avoided.
When drilling with a floating rig, it must be able to move off location
away from the well. This might be due to bad weather forcing operations
to be suspended, for instance. The BOP system has to be capable of
latching to and releasing from the wellhead, so at the bottom of the BOP
is a hydraulic latch. Also the riser (described in chapter 4) must be capable
of being released, leaving the BOP on the seabed, and so another hydraulic
latch is placed here. As floating rigs do move to some extent, the riser
and BOP system must accommodate some angular movement of the
_Devereux_Book.indb 266 1/16/12 2:12 PM