Page 244 - Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
P. 244
2 7 6 Dust Explosions in the Process Industries
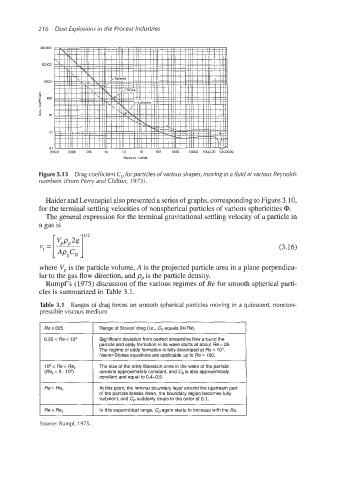
Figure 3.13 Drag coefficient C, for particles of various shapes, moving in a fluid at various Reynolds
numbers (From Perry and Chilton, 1973).
Haider and Levenspiel also presented a series of graphs,corresponding to Figure 3.10,
for the terminal settling velocities of nonspherical particles of various sphericities a.
The general expression for the terminal gravitational settling velocity of a particle in
a gas is
(3.16)
where V, is the particle volume, A is the projected particle area in a plane perpendicu-
lar to the gas flow direction, and ppis the particle density.
Rumpf’s (1975) discussion of the various regimes of Re for smooth spherical parti-
cles is summarized in Table 3.1,
Table 3.1 Ranges of drag forces on smooth spherical particles moving in a quiescent, noncom-
pressible viscous medium
I GO025 ~ I Range of Stokes’drag (i.e.2, equals 24/Re).
0.25<Re<103 Significant deviation from perfect streamline flow around the
particle and eddy formation in its wake starts at about Re = 25.
The regime of eddy formation is fully developed at Re = lo3.
Navier-Stokesequations are applicable up to Re = 100.
lo3< Re< Re, The size of the eddy liberation zone in the wake of the particle
(Rec=3.lo5) remains approximately constant, and C, is also approximately
constant and equal to 0.4-0.5.
Re = Re, At this point, the laminar boundary layer around the upstream part
of the particle breaks down, the boundary region becomes fully
turbulent, and C, suddenly drops to the order of 0.1.
Re > Re, In this supercritical range, C,again starts to increase with the Re.