Page 184 - Dynamics of Mechanical Systems
P. 184
0593_C06_fm Page 165 Monday, May 6, 2002 2:28 PM
Forces and Force Systems 165
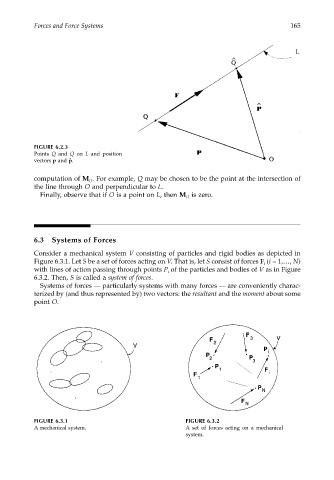
FIGURE 6.2.3
Points Q and Q on L and position
vectors p and ˆ p.
computation of M . For example, Q may be chosen to be the point at the intersection of
O
the line through O and perpendicular to L.
Finally, observe that if O is a point on L, then M is zero.
O
6.3 Systems of Forces
Consider a mechanical system V consisting of particles and rigid bodies as depicted in
Figure 6.3.1. Let S be a set of forces acting on V. That is, let S consist of forces F (i = 1,…, N)
i
with lines of action passing through points P of the particles and bodies of V as in Figure
i
6.3.2. Then, S is called a system of forces.
Systems of forces — particularly systems with many forces — are conveniently charac-
terized by (and thus represented by) two vectors: the resultant and the moment about some
point O.
FIGURE 6.3.1 FIGURE 6.3.2
A mechanical system. A set of forces acting on a mechanical
system.