Page 372 - Earth's Climate Past and Future
P. 372
348 PART V • Historical and Future Climate Change
and carbon aerosol input to the atmosphere could Myr ago
produce a cooling effect that would counter part of 21 0 25 50
the future CO warming but by probably only a small
2 Earth history
fraction.
20
4 × CO 2
Future Climate Changes Caused by Path
Increased CO 19
2
As atmospheric CO levels rise in the future, Earth’s cli-
2 Earth history
mate will continue to warm. Attempts to estimate the Global temperature (°C) 18
amount of future warming are subject to the cumulative
uncertainties from three factors: the amount of excess
CO emitted by humans, the levels of atmospheric CO 17 2 × CO 2
2 2
reached as the excess carbon is redistributed among var- Path
ious carbon reservoirs, and Earth’s sensitivity to higher 16
CO concentrations. Emissions of other greenhouse
2
gases are also a source of uncertainty.
The two projections of future CO concentra- 15
2 0 100 200 300 400 500
tions shown in Figure 19–3 span the possible range of Years in the future
increases during the next few centuries. The best esti-
mate of Earth’s sensitivity to a doubling of CO is FIGURE 19-6 Temperature: Past and future Average
2
2.5°C, a value that falls in the middle of the range indi- global temperature in the next 200 years is projected to reach
cated by climate models (Chapter 18). Two estimates of levels comparable to those that last occurred many millions
projected future temperature change based on this cli- of years ago.
mate sensitivity are plotted in Figure 19–5. The lower
projection shows the amount of warming for the emis-
sions trend that drives atmospheric CO concentrations
2 to twice their preindustrial value (the 2 × CO case).
2
The result is an additional 2°C warming by the year
2100, with further warming into the early 2100s. For
this projection, the full warming (industrial era and
future) by 2100 is 2.5°C.
20 The upper projection shows the additional warming
4 × CO 2 for the emissions pathway that reaches four times the
Path
Global temperature (°C) 18 and the peak warming is more than 5°C. A future
preindustrial CO level (the 4 × CO case). In this pro-
2
2
19
jection, an additional warming of 3.8°C occurs by 2100
warming of this amount would be more than 7 times the
warming during the 1900s.
17
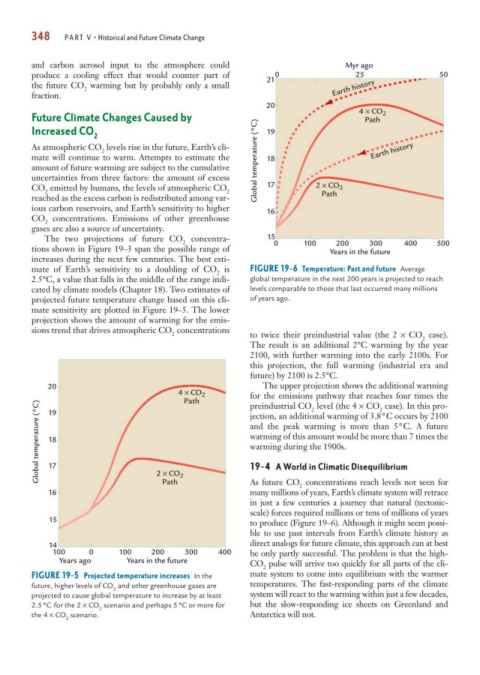
19-4 A World in Climatic Disequilibrium
2 × CO
2
As future CO concentrations reach levels not seen for
Path
2
16 many millions of years, Earth’s climate system will retrace
in just a few centuries a journey that natural (tectonic-
scale) forces required millions or tens of millions of years
15
to produce (Figure 19–6). Although it might seem possi-
ble to use past intervals from Earth’s climate history as
14 direct analogs for future climate, this approach can at best
100 0 100 200 300 400 be only partly successful. The problem is that the high-
Years ago Years in the future
CO pulse will arrive too quickly for all parts of the cli-
2
FIGURE 19-5 Projected temperature increases In the mate system to come into equilibrium with the warmer
future, higher levels of CO and other greenhouse gases are temperatures. The fast-responding parts of the climate
2
projected to cause global temperature to increase by at least system will react to the warming within just a few decades,
2.5°C for the 2 × CO scenario and perhaps 5°C or more for but the slow-responding ice sheets on Greenland and
2
the 4 × CO scenario. Antarctica will not.
2