Page 263 - Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
P. 263
260 Electric Drives and Electromechanical Systems
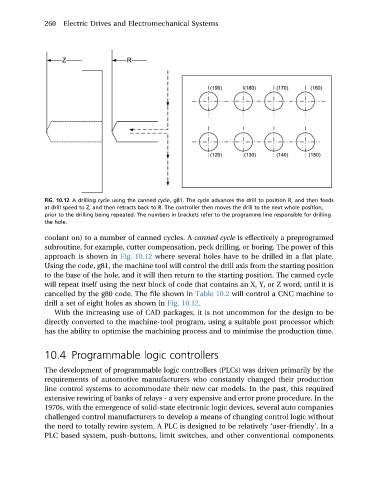
FIG. 10.12 A drilling cycle using the canned cycle, g81. The cycle advances the drill to position R, and then feeds
at drill speed to Z, and then retracts back to R. The controller then moves the drill to the next whole position,
prior to the drilling being repeated. The numbers in brackets refer to the programme line responsible for drilling
the hole.
coolant on) to a number of canned cycles. A canned cycle is effectively a preprogramed
subroutine, for example, cutter compensation, peck drilling, or boring. The power of this
approach is shown in Fig. 10.12 where several holes have to be drilled in a flat plate.
Using the code, g81, the machine tool will control the drill axis from the starting position
to the base of the hole, and it will then return to the starting position. The canned cycle
will repeat itself using the next block of code that contains an X, Y, or Z word, until it is
cancelled by the g80 code. The file shown in Table 10.2 will control a CNC machine to
drill a set of eight holes as shown in Fig. 10.12.
With the increasing use of CAD packages, it is not uncommon for the design to be
directly converted to the machine-tool program, using a suitable post processor which
has the ability to optimise the machining process and to minimise the production time.
10.4 Programmable logic controllers
The development of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) was driven primarily by the
requirements of automotive manufacturers who constantly changed their production
line control systems to accommodate their new car models. In the past, this required
extensive rewiring of banks of relays - a very expensive and error prone procedure. In the
1970s, with the emergence of solid-state electronic logic devices, several auto companies
challenged control manufacturers to develop a means of changing control logic without
the need to totally rewire system. A PLC is designed to be relatively ‘user-friendly’. In a
PLC based system, push-buttons, limit switches, and other conventional components