Page 68 - Electric Machinery Fundamentals
P. 68
44 ELECTRIC MACHINERY FUNDAMENTALS
B = 0.1 T,
OJ!l
~ X X X
,
AAA
directed into the page
+
==- 120 V eind 10m
X X X
Ca)
8=0.1 T,
0.3!l
AA directed into the page
V
X X X
F ind -30N +
~~ 120V _ e ind _ F(IPP= 30 N
v
X X X
Cb) 8=0.1 T,
0.3!l
. A directed into the page
" X X X
~~ 20V
1
F 1ood = 30N
~-----=-1
X X X
(e)
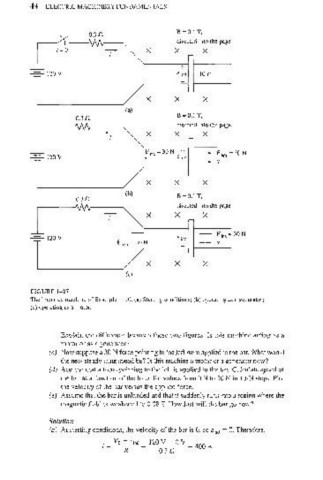
FIGURE 1-27
The linear de machine of Example 1-10, (a) Starting conditions; (b) operating as a generator;
(c) operating as a motor.
Explain the difference between these two figures. Is this machine acting as a
motor or as a generator?
(c) Now suppose a 30¥N force pointing to the Jeft were applied LO the bar. What would
the new steady-state speed be? Is this machine a motor or a generator now?
(d) Assume that a force pointing to the left is applied to the bar. Calculate speed of
the bar as a function of the force for values from 0 N La 50 N in I O-N steps. Plot
the velocity of the bar versus the applied force.
(e) Assume that the bar is unloaded and that it suddenly runs into a region where the
magnetic field is weakened to 0.08 T. How fast will the bar go now?
Solution
(a) At starting conditions, the velocity of the bar is 0, so ej lld = O. Therefore,
120 V - 0 V
i= - V,,-B -C-o-e-"i'",d 400 A
R
0.3 [l