Page 166 - Electrical Installation in Hazardous Area
P. 166
132 Electrical installations in hazardous areas
Hip
Ground
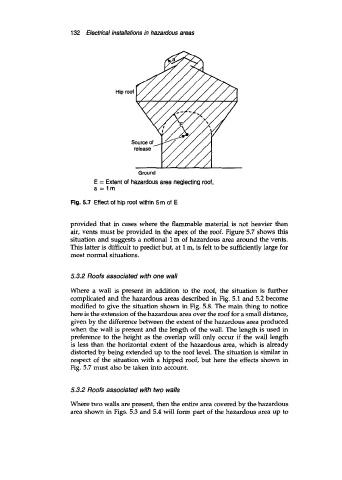
E = Extent of hazardous area neglecting roof,
a=lm
Fig. 5.7 Effect of hip roof within 5m of E
provided that in cases where the flammable material is not heavier than
air, vents must be provided in the apex of the roof. Figure 5.7 shows this
situation and suggests a notional 1 m of hazardous area around the vents.
This latter is difficult to predict but, at 1 m, is felt to be sufficiently large for
most normal situations.
5.3.2 Roofs associated with one wall
Where a wall is present in addition to the roof, the situation is further
complicated and the hazardous areas described in Fig. 5.1 and 5.2 become
modified to give the situation shown in Fig. 5.8. The main thing to notice
here is the extension of the hazardous area over the roof for a small distance,
given by the difference between the extent of the hazardous area produced
when the wall is present and the length of the wall. The length is used in
preference to the height as the overlap will only occur if the wall length
is less than the horizontal extent of the hazardous area, which is already
distorted by being extended up to the roof level. The situation is similar in
respect of the situation with a hipped roof, but here the effects shown in
Fig. 5.7 must also be taken into account.
5.3.2 Roofs associated with two walls
Where two walls are present, then the entire area covered by the hazardous
area shown in Figs. 5.3 and 5.4 will form part of the hazardous area up to