Page 440 - Electrical Properties of Materials
P. 440
422 Artificial materials or metamaterials
Hyperlens
Imge
Ag/Al O
2 3
multilayers
Cr
Object
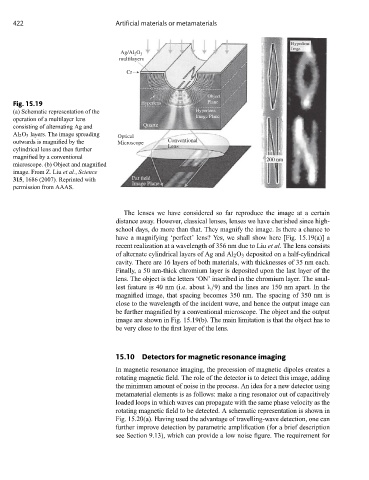
Fig. 15.19 Hyperlens Plane
(a) Schematic representation of the Hyperlens
Image Plane
operation of a multilayer lens
consisting of alternating Ag and Quartz
Al 2 O 3 layers. The image spreading Optical
outwards is magnified by the Microscope Conventional
cylindrical lens and then further Lens
magnified by a conventional
200 nm
microscope. (b) Object and magnified
image. From Z. Liu et al., Science
315, 1686 (2007). Reprinted with Far field
Image Plane
permission from AAAS.
The lenses we have considered so far reproduce the image at a certain
distance away. However, classical lenses, lenses we have cherished since high-
school days, do more than that. They magnify the image. Is there a chance to
have a magnifying ‘perfect’ lens? Yes, we shall show here [Fig. 15.19(a)] a
recent realization at a wavelength of 356 nm due to Liu et al. The lens consists
of alternate cylindrical layers of Ag and Al 2 O 3 deposited on a half-cylindrical
cavity. There are 16 layers of both materials, with thicknesses of 35 nm each.
Finally, a 50 nm-thick chromium layer is deposited upon the last layer of the
lens. The object is the letters ‘ON’ inscribed in the chromium layer. The smal-
lest feature is 40 nm (i.e. about λ/9) and the lines are 150 nm apart. In the
magnified image, that spacing becomes 350 nm. The spacing of 350 nm is
close to the wavelength of the incident wave, and hence the output image can
be further magnified by a conventional microscope. The object and the output
image are shown in Fig. 15.19(b). The main limitation is that the object has to
be very close to the first layer of the lens.
15.10 Detectors for magnetic resonance imaging
In magnetic resonance imaging, the precession of magnetic dipoles creates a
rotating magnetic field. The role of the detector is to detect this image, adding
the minimum amount of noise in the process. An idea for a new detector using
metamaterial elements is as follows: make a ring resonator out of capacitively
loaded loops in which waves can propagate with the same phase velocity as the
rotating magnetic field to be detected. A schematic representation is shown in
Fig. 15.20(a). Having used the advantage of travelling-wave detection, one can
further improve detection by parametric amplification (for a brief description
see Section 9.13), which can provide a low noise figure. The requirement for