Page 174 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 174
136 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
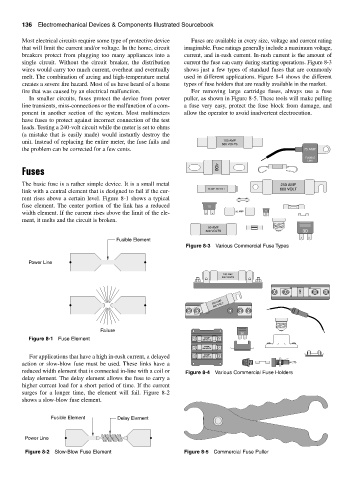
Most electrical circuits require some type of protective device Fuses are available in every size, voltage and current rating
that will limit the current and/or voltage. In the home, circuit imaginable. Fuse ratings generally include a maximum voltage,
breakers protect from plugging too many appliances into a current, and in-rush current. In-rush current is the amount of
single circuit. Without the circuit breaker, the distribution current the fuse can carry during starting operations. Figure 8-3
wires would carry too much current, overheat and eventually shows just a few types of standard fuses that are commonly
melt. The combination of arcing and high-temperature metal used in different applications. Figure 8-4 shows the different
creates a severe fire hazard. Most of us have heard of a home types of fuse holders that are readily available in the market.
fire that was caused by an electrical malfunction. For removing large cartridge fuses, always use a fuse
In smaller circuits, fuses protect the device from power puller, as shown in Figure 8-5. These tools will make pulling
line transients, miss-connections or the malfunction of a com- a fuse very easy, protect the fuse block from damage, and
ponent in another section of the system. Most multimeters allow the operator to avoid inadvertent electrocution.
have fuses to protect against incorrect connection of the test
leads. Testing a 240-volt circuit while the meter is set to ohms
(a mistake that is easily made) would instantly destroy the
unit. Instead of replacing the entire meter, the fuse fails and 100 AMP
500 VOLTS
the problem can be corrected for a few cents. 75 AMP
FUSIBLE
LINK
Fuses 400
The basic fuse is a rather simple device. It is a small metal 250 AMP
link with a central element that is designed to fail if the cur- 30 AMP 500 VOLT 600 VOLT
rent rises above a certain level. Figure 8-1 shows a typical
fuse element. The center portion of the link has a reduced 10
width element. If the current rises above the limit of the ele- 20 AMP 5
ment, it melts and the circuit is broken.
50 AMP
300 VOLTS 30
Fusible Element
Figure 8-3 Various Commercial Fuse Types
Power Line
100 AMP
500 VOLTS
250 AMP 350
600 VOLT
Failure
30
Figure 8-1 Fuse Element 300 VOLTS
30 AMP
30 AMP
300 VOLTS
30 AMP
For applications that have a high in-rush current, a delayed 300 VOLTS
action or slow-blow fuse must be used. These links have a
reduced width element that is connected in-line with a coil or Figure 8-4 Various Commercial Fuse Holders
delay element. The delay element allows the fuse to carry a
higher current load for a short period of time. If the current
surges for a longer time, the element will fail. Figure 8-2
shows a slow-blow fuse element.
Fusible Element Delay Element
Power Line
Figure 8-2 Slow-Blow Fuse Element Figure 8-5 Commercial Fuse Puller