Page 225 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 225
Chapter 10 Wire and Conductors 187
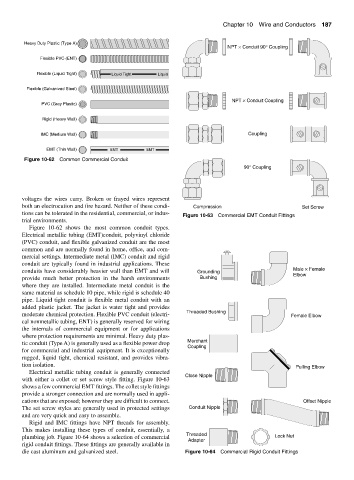
Heavy Duty Plastic (Type A)
NPT × Conduit 90° Coupling
Flexible PVC (ENT)
Flexible (Liquid Tight) Liquid Tight Liquid
Flexible (Galvanized Steel)
NPT × Conduit Coupling
PVC (Gray Plastic)
Rigid (Heavy Wall)
IMC (Medium Wall) Coupling
EMT (Thin Wall) EMT EMT
Figure 10-62 Common Commercial Conduit
90° Coupling
voltages the wires carry. Broken or frayed wires represent
both an electrocution and fire hazard. Neither of these condi- Compression Set Screw
tions can be tolerated in the residential, commercial, or indus- Figure 10-63 Commercial EMT Conduit Fittings
trial environments.
Figure 10-62 shows the most common conduit types.
Electrical metallic tubing (EMT)conduit, polyvinyl chloride
(PVC) conduit, and flexible galvanized conduit are the most
common and are normally found in home, office, and com-
mercial settings. Intermediate metal (IMC) conduit and rigid
conduit are typically found in industrial applications. These
conduits have considerably heavier wall than EMT and will Grounding Male × Female
Elbow
provide much better protection in the harsh environments Bushing
where they are installed. Intermediate metal conduit is the
same material as schedule 10 pipe, while rigid is schedule 40
pipe. Liquid tight conduit is flexible metal conduit with an
added plastic jacket. The jacket is water tight and provides
Threaded Bushing
moderate chemical protection. Flexible PVC conduit (electri- Female Elbow
cal nonmetallic tubing, ENT) is generally reserved for wiring
the internals of commercial equipment or for applications
where protection requirements are minimal. Heavy duty plas-
tic conduit (Type A) is generally used as a flexible power drop Merchant
Coupling
for commercial and industrial equipment. It is exceptionally
rugged, liquid tight, chemical resistant, and provides vibra-
tion isolation. Pulling Elbow
Electrical metallic tubing conduit is generally connected
Close Nipple
with either a collet or set screw style fitting. Figure 10-63
shows a few commercial EMT fittings. The collet style fittings
provide a stronger connection and are normally used in appli-
cations that are exposed; however they are difficult to connect. Offset Nipple
The set screw styles are generally used in protected settings Conduit Nipple
and are very quick and easy to assemble.
Rigid and IMC fittings have NPT threads for assembly.
This makes installing these types of conduit, essentially, a
Threaded
plumbing job. Figure 10-64 shows a selection of commercial Lock Nut
Adapter
rigid conduit fittings. These fittings are generally available in
die cast aluminum and galvanized steel. Figure 10-64 Commercial Rigid Conduit Fittings