Page 312 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 312
274 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
Simply stated, electrostatics is the study of electrical energy simply a glass jar with a piece of folded foil hanging from a
at rest. Any time a conductor is at a potential, it exhibits a nat- metal frame, which is connected to a terminal. When a
ural tendency to equalize the charge state with an opposite charge is applied to the terminal, the entire metal frame and
charge. Similarly, the conductor exhibits a natural tendency to both tabs of the foil adopt the same charge potential. The
repel like charge states. hanging tabs, having the same charge potential, repel each
other and the tab’s visible deflection is in direct proportion
to the voltage applied. Electroscopes are very simple devices
Electrostatic Voltmeters to build and provide an excellent introduction to the study of
electrostatics.
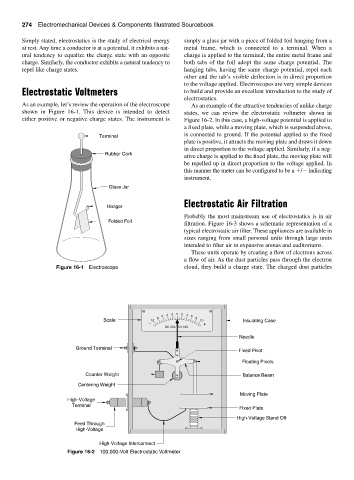
As an example, let’s review the operation of the electroscope As an example of the attractive tendencies of unlike charge
shown in Figure 16-1. This device is intended to detect states, we can review the electrostatic voltmeter shown in
either positive or negative charge states. The instrument is Figure 16-2. In this case, a high-voltage potential is applied to
a fixed plate, while a moving plate, which is suspended above,
is connected to ground. If the potential applied to the fixed
Terminal
plate is positive, it attracts the moving plate and draws it down
in direct proportion to the voltage applied. Similarly, if a neg-
Rubber Cork
ative charge is applied to the fixed plate, the moving plate will
be repelled up in direct proportion to the voltage applied. In
this manner the meter can be configured to be a / indicating
instrument.
Glass Jar
Electrostatic Air Filtration
Hanger
Probably the most mainstream use of electrostatics is in air
Folded Foil
filtration. Figure 16-3 shows a schematic representation of a
typical electrostatic air filter. These appliances are available in
sizes ranging from small personal units through large units
intended to filter air in expansive arenas and auditoriums.
These units operate by creating a flow of electrons across
a flow of air. As the dust particles pass through the electron
Figure 16-1 Electroscope cloud, they build a charge state. The charged dust particles
6 4 2 0 2 4 6
Scale 10 8 8 10 Insulating Case
− +
DC VOLTS x 10K
Needle
Ground Terminal
Fixed Pivot
Floating Pivots
Counter Weight Balance Beam
Centering Weight
Moving Plate
High-Voltage
Terminal
Fixed Plate
High-Voltage Stand Off
Feed Through
High-Voltage
High-Voltage Interconnect
Figure 16-2 100,000-Volt Electrostatic Voltmeter