Page 307 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 307
Chapter 15 Sensors 269
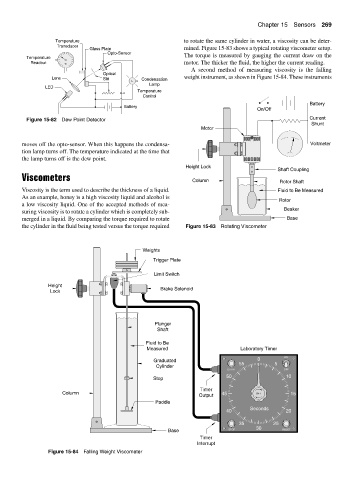
Temperature to rotate the same cylinder in water, a viscosity can be deter-
Transducer
Glass Plate mined. Figure 15-83 shows a typical rotating viscometer setup.
Opto-Sensor
Temperature The torque is measured by gauging the current draw on the
Readout °F motor. The thicker the fluid, the higher the current reading.
A second method of measuring viscosity is the falling
Optical
Lens Slit Condensation weight instrument, as shown in Figure 15-84. These instruments
L
Lamp
LED
Temperature
Control
Battery
Battery
On/Off
Figure 15-82 Dew Point Detector Current
Shunt
Motor
moves off the opto-sensor. When this happens the condensa- Voltmeter
tion lamp turns off. The temperature indicated at the time that
the lamp turns off is the dew point.
Height Lock
Shaft Coupling
Viscometers Column Rotor Shaft
Viscosity is the term used to describe the thickness of a liquid. Fluid to Be Measured
As an example, honey is a high viscosity liquid and alcohol is
Rotor
a low viscosity liquid. One of the accepted methods of mea-
Beaker
suring viscosity is to rotate a cylinder which is completely sub-
merged in a liquid. By comparing the torque required to rotate Base
the cylinder in the fluid being tested versus the torque required Figure 15-83 Rotating Viscometer
Weights
Trigger Plate
Limit Switch
Height
Lock Brake Solenoid
Plunger
Shaft
Fluid to Be
Measured Laboratory Timer
Graduated 0 ON
Cylinder 55 5
START OFF
Stop 50 10
Timer
Column 45 SET 15
Output
Paddle
Seconds
40 20
35 25
30
Base STOP RESET
Timer
Interrupt
Figure 15-84 Falling Weight Viscometer