Page 306 - Electromechanical Devices and Components Illustrated Sourcebook
P. 306
268 Electromechanical Devices & Components Illustrated Sourcebook
Accelerometer Salt Impregnated Paper
Mount Holes
Noncorosive Metal
Washer Plastic Voltmeter
Base
1 2 3
4
+/− Reading DC VOLTS
Voltmeter
+ −
Moisture
Calibration Detector
Potentiometer
Fixed Resistor
+ − + −
Sensitivity
Potentiometer
Batteries
Battery
Figure 15-79 Accelerometer Schematic
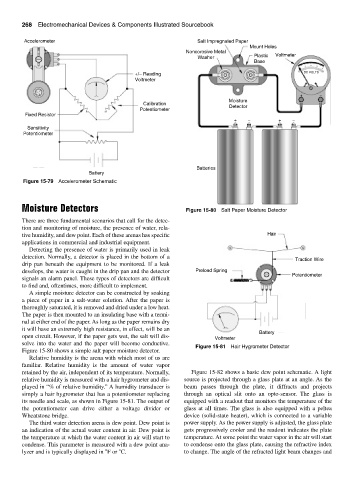
Moisture Detectors Figure 15-80 Salt Paper Moisture Detector
There are three fundamental scenarios that call for the detec-
tion and monitoring of moisture, the presence of water, rela-
tive humidity, and dew point. Each of these arenas has specific Hair
applications in commercial and industrial equipment.
Detecting the presence of water is primarily used in leak
detection. Normally, a detector is placed in the bottom of a
Traction Wire
drip pan beneath the equipment to be monitored. If a leak
develops, the water is caught in the drip pan and the detector Preload Spring
Potentiometer
signals an alarm panel. These types of detectors are difficult
to find and, oftentimes, more difficult to implement.
A simple moisture detector can be constructed by soaking
a piece of paper in a salt-water solution. After the paper is
thoroughly saturated, it is removed and dried under a low heat.
The paper is then mounted to an insulating base with a termi-
nal at either end of the paper. As long as the paper remains dry
it will have an extremely high resistance, in effect, will be an
Battery
open circuit. However, if the paper gets wet, the salt will dis- Voltmeter
solve into the water and the paper will become conductive.
Figure 15-81 Hair Hygrometer Detector
Figure 15-80 shows a simple salt paper moisture detector.
Relative humidity is the arena with which most of us are
familiar. Relative humidity is the amount of water vapor
retained by the air, independent of its temperature. Normally, Figure 15-82 shows a basic dew point schematic. A light
relative humidity is measured with a hair hygrometer and dis- source is projected through a glass plate at an angle. As the
played in “% of relative humidity.” A humidity transducer is beam passes through the plate, it diffracts and projects
simply a hair hygrometer that has a potentiometer replacing through an optical slit onto an opto-sensor. The glass is
its needle and scale, as shown in Figure 15-81. The output of equipped with a readout that monitors the temperature of the
the potentiometer can drive either a voltage divider or glass at all times. The glass is also equipped with a peltea
Wheatstone bridge. device (solid-state heater), which is connected to a variable
The third water detection arena is dew point. Dew point is power supply. As the power supply is adjusted, the glass plate
an indication of the actual water content in air. Dew point is gets progressively cooler and the readout indicates the plate
the temperature at which the water content in air will start to temperature. At some point the water vapor in the air will start
condense. This parameter is measured with a dew point ana- to condense onto the glass plate, causing the refractive index
lyzer and is typically displayed in F or C. to change. The angle of the refracted light beam changes and