Page 322 -
P. 322
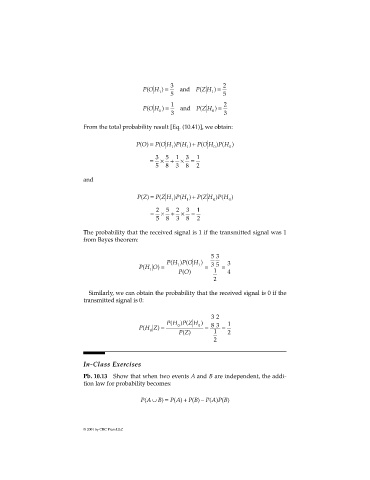
PO H( ) = 3 and P Z H( ) = 2
1 1
5 5
PO H( ) = 1 and P Z H( ) = 2
0 0
3 3
From the total probability result [Eq. (10.41)], we obtain:
PO() = PO H P H( ) ( ) + P O H P H( ) ( )
1 1 0 0
= 3 × 5 + 1 × 3 = 1
5 8 3 8 2
and
PZ() = PZ H P H( ) ( ) + P Z H P H( ) ( )
1 1 0 0
= 2 × 5 + 2 × 3 = 1
5 8 3 8 2
The probability that the received signal is 1 if the transmitted signal was 1
from Bayes theorem:
5 3
PH P O H( ) ( ) 3
PH O( ) = 1 1 = 3 5 =
1 1
PO() 4
2
Similarly, we can obtain the probability that the received signal is 0 if the
transmitted signal is 0:
3 2
PH P Z H( 0 ) ( 0 ) 1
PH Z( ) = = 8 3 =
0 1
PZ() 2
2
In-Class Exercises
Pb. 10.13 Show that when two events A and B are independent, the addi-
tion law for probability becomes:
PA( ∪ B) = P A() + P B( ) − P A P B() ( )
© 2001 by CRC Press LLC