Page 122 - Bruno Linder Elementary Physical Chemistry
P. 122
August 18, 2010 11:37 9in x 6in b985-ch10 Elementary Physical Chemistry
Quantum Theory. The Chemical Bond 107
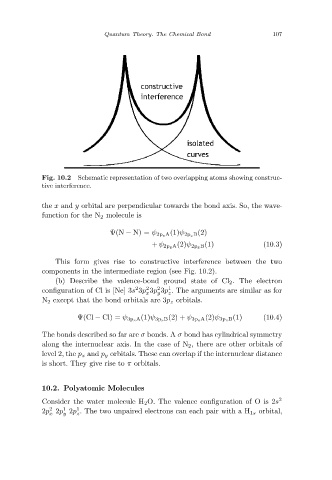
Schematic representation of two overlapping atoms showing construc-
Fig. 10.2
tive interference.
the x and y orbital are perpendicular towards the bond axis. So, the wave-
function for the N 2 molecule is
Ψ(N − N) = ψ 2p zA (1)ψ 2p zB (2)
+ ψ 2p z A(2)ψ 2p z B (1) (10.3)
This form gives rise to constructive interference between the two
components in the intermediate region (see Fig. 10.2).
(b) Describe the valence-bond ground state of Cl 2. The electron
1
2
2
2
configuration of Cl is [Ne] 3s 3p 3p 3p . The arguments are similar as for
y
z
x
N 2 except that the bond orbitals are 3p z orbitals.
Ψ(Cl − Cl) = ψ 3p z A(1)ψ 3p z B (2) + ψ 3p z A(2)ψ 3p z B (1) (10.4)
The bonds described so far are σ bonds. A σ bond has cylindrical symmetry
along the internuclear axis. In the case of N 2, there are other orbitals of
level 2, the p x and p y orbitals. These can overlap if the internuclear distance
is short. They give rise to π orbitals.
10.2. Polyatomic Molecules
Consider the water molecule H 2O. The valence configuration of O is 2s 2
1
1
2
2p 2p 2p . The two unpaired electrons can each pair with a H 1s orbital,
x
y
z