Page 99 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 99
P1: GNB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN005F-954 June 15, 2001 20:48
812 Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors
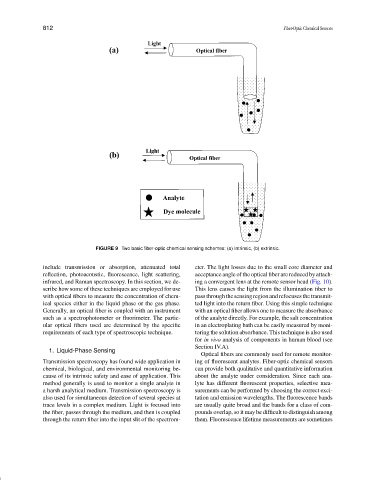
FIGURE 9 Two basic fiber-optic chemical sensing schemes: (a) Intrinsic, (b) extrinsic.
include transmission or absorption, attenuated total eter. The light losses due to the small core diameter and
reflection, photoacoustic, fluorescence, light scattering, acceptance angle of the optical fiber are reduced by attach-
infrared, and Raman spectroscopy. In this section, we de- ing a convergent lens at the remote sensor head (Fig. 10).
scribe how some of these techniques are employed for use This lens causes the light from the illumination fiber to
with optical fibers to measure the concentration of chem- passthroughthesensingregionandrefocusesthetransmit-
ical species either in the liquid phase or the gas phase. ted light into the return fiber. Using this simple technique
Generally, an optical fiber is coupled with an instrument with an optical fiber allows one to measure the absorbance
such as a spectrophotometer or fluorimeter. The partic- of the analyte directly. For example, the salt concentration
ular optical fibers used are determined by the specific in an electroplating bath can be easily measured by moni-
requirements of each type of spectroscopic technique. toring the solution absorbance. This technique is also used
for in vivo analysis of components in human blood (see
Section IV.A).
1. Liquid-Phase Sensing
Optical fibers are commonly used for remote monitor-
Transmission spectroscopy has found wide application in ing of fluorescent analytes. Fiber-optic chemical sensors
chemical, biological, and environmental monitoring be- can provide both qualitative and quantitative information
cause of its intrinsic safety and ease of application. This about the analyte under consideration. Since each ana-
method generally is used to monitor a single analyte in lyte has different fluorescent properties, selective mea-
a harsh analytical medium. Transmission spectroscopy is surements can be performed by choosing the correct exci-
also used for simultaneous detection of several species at tation and emission wavelengths. The fluorescence bands
trace levels in a complex medium. Light is focused into are usually quite broad and the bands for a class of com-
the fiber, passes through the medium, and then is coupled pounds overlap, so it may be difficult to distinguish among
through the return fiber into the input slit of the spectrom- them. Fluorescence lifetime measurements are sometimes