Page 97 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 97
P1: GNB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN005F-954 June 15, 2001 20:48
810 Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors
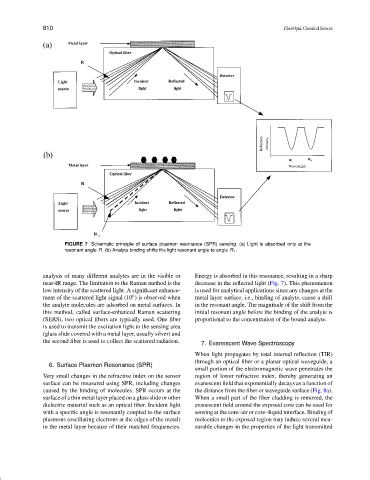
FIGURE 7 Schematic principle of surface plasmon resonance (SPR) sensing. (a) Light is absorbed only at the
resonant angle R. (b) Analyte binding shifts the light resonant angle to angle R 1 .
analysis of many different analytes are in the visible or Energy is absorbed in this resonance, resulting in a sharp
near-IR range. The limitation to the Raman method is the decrease in the reflected light (Fig. 7). This phenomenon
low intensity of the scattered light. A significant enhance- is used for analytical applications since any changes at the
6
ment of the scattered light signal (10 ) is observed when metal layer surface, i.e., binding of analyte, cause a shift
the analyte molecules are adsorbed on metal surfaces. In in the resonant angle. The magnitude of the shift from the
this method, called surface-enhanced Raman scattering initial resonant angle before the binding of the analyte is
(SERS), two optical fibers are typically used. One fiber proportional to the concentration of the bound analyte.
is used to transmit the excitation light to the sensing area
(glass slide covered with a metal layer, usually silver) and
the second fiber is used to collect the scattered radiation. 7. Evanescent Wave Spectroscopy
When light propagates by total internal reflection (TIR)
through an optical fiber or a planar optical waveguide, a
6. Surface Plasmon Resonance (SPR)
small portion of the electromagnetic wave penetrates the
Very small changes in the refractive index on the sensor region of lower refractive index, thereby generating an
surface can be measured using SPR, including changes evanescent field that exponentially decays as a function of
caused by the binding of molecules. SPR occurs at the the distance from the fiber or waveguide surface (Fig. 8a).
surface of a thin metal layer placed on a glass slide or other When a small part of the fiber cladding is removed, the
dielectric material such as an optical fiber. Incident light evanescent field around the exposed core can be used for
with a specific angle is resonantly coupled to the surface sensing at the core–air or core–liquid interface. Binding of
plasmons (oscillating electrons at the edges of the metal) molecules to the exposed region may induce several mea-
in the metal layer because of their matched frequencies. surable changes in the properties of the light transmitted