Page 98 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 98
P1: GNB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN005F-954 June 15, 2001 20:48
Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors 811
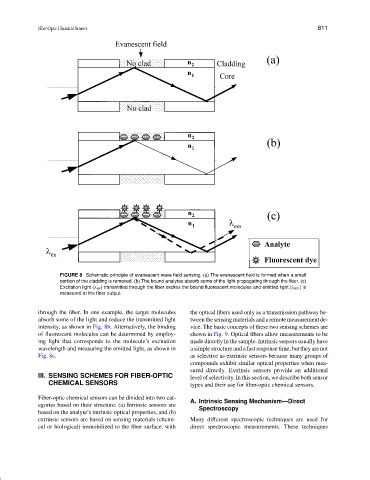
FIGURE 8 Schematic principle of evanescent wave field sensing. (a) The evanescent field is formed when a small
portion of the cladding is removed. (b) The bound analytes absorb some of the light propagating through the fiber. (c)
Excitation light (λ ex ) transmitted through the fiber excites the bound fluorescent molecules and emitted light (λ em )is
measured at the fiber output.
through the fiber. In one example, the target molecules the optical fibers used only as a transmission pathway be-
absorb some of the light and reduce the transmitted light tween the sensing materials and a remote measurement de-
intensity, as shown in Fig. 8b. Alternatively, the binding vice. The basic concepts of these two sensing schemes are
of fluorescent molecules can be determined by employ- shown in Fig. 9. Optical fibers allow measurements to be
ing light that corresponds to the molecule’s excitation made directly in the sample. Intrinsic sensors usually have
wavelength and measuring the emitted light, as shown in a simple structure and a fast response time, but they are not
Fig. 8c. as selective as extrinsic sensors because many groups of
compounds exhibit similar optical properties when mea-
sured directly. Extrinsic sensors provide an additional
III. SENSING SCHEMES FOR FIBER-OPTIC level of selectivity. In this section, we describe both sensor
CHEMICAL SENSORS types and their use for fiber-optic chemical sensors.
Fiber-optic chemical sensors can be divided into two cat-
A. Intrinsic Sensing Mechanism—Direct
egories based on their structure: (a) Intrinsic sensors are
Spectroscopy
based on the analyte’s intrinsic optical properties, and (b)
extrinsic sensors are based on sensing materials (chemi- Many different spectroscopic techniques are used for
cal or biological) immobilized to the fiber surface, with direct spectroscopic measurements. These techniques