Page 93 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioTechnology
P. 93
P1: GNB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN005F-954 June 15, 2001 20:48
806 Fiber-Optic Chemical Sensors
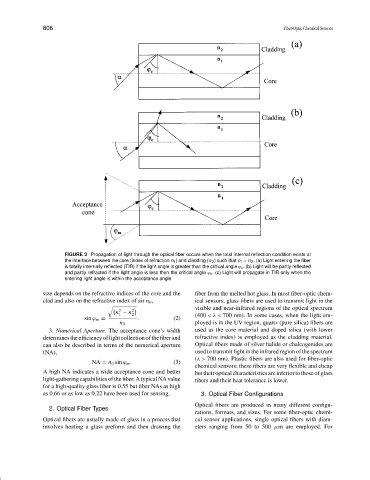
FIGURE 3 Propagation of light through the optical fiber occurs when the total internal reflection condition exists at
the interface between the core (index of refraction n 1 ) and cladding (n 2 ) such that n 1 > n 2 . (a) Light entering the fiber
is totally internally reflected (TIR) if the light angle is greater than the critical angle ϕ c . (b) Light will be partly reflected
and partly refracted if the light angle is less then the critical angle ϕ c . (c) Light will propagate in TIR only when the
entering light angle is within the acceptance angle.
size depends on the refractive indices of the core and the fiber from the melted hot glass. In most fiber-optic chem-
clad and also on the refractive index of air n 0 , ical sensors, glass fibers are used to transmit light in the
visible and near-infrared regions of the optical spectrum
2 2
n − n
1 2 (400 <λ< 700 nm). In some cases, when the light em-
sin ϕ m = . (2)
n 0 ployed is in the UV region, quartz (pure silica) fibers are
3. Numerical Aperture. The acceptance cone’s width used as the core material and doped silica (with lower
determinestheefficiencyoflightcollectionofthefiberand refractive index) is employed as the cladding material.
can also be described in terms of the numerical aperture Optical fibers made of silver halide or chalcogenides are
(NA), used to transmit light in the infrared region of the spectrum
(λ> 700 nm). Plastic fibers are also used for fiber-optic
NA = n 0 sin ϕ m . (3)
chemical sensors; these fibers are very flexible and cheap
A high NA indicates a wide acceptance cone and better buttheiropticalcharacteristicsareinferiortothoseofglass
light-gathering capabilities of the fiber. A typical NA value fibers and their heat tolerance is lower.
for a high-quality glass fiber is 0.55 but fiber NAs as high
as 0.66 or as low as 0.22 have been used for sensing. 3. Optical Fiber Configurations
Optical fibers are produced in many different configu-
2. Optical Fiber Types
rations, formats, and sizes. For some fiber-optic chemi-
Optical fibers are usually made of glass in a process that cal sensor applications, single optical fibers with diam-
involves heating a glass preform and then drawing the eters ranging from 50 to 500 µm are employed. For