Page 172 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 172
P1: GGY Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN004D-156 June 8, 2001 15:28
Cryogenic Process Engineering 15
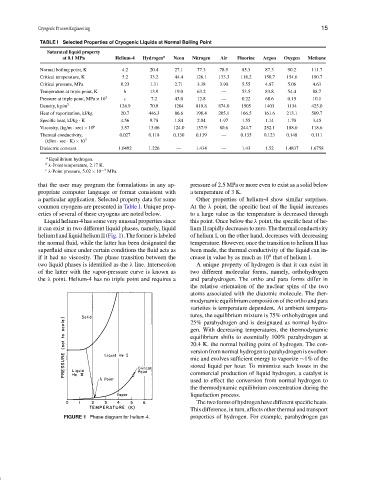
TABLE I Selected Properties of Cryogenic Liquids at Normal Boiling Point
Saturated liquid property
at 0.1 MPa Helium-4 Hydrogen a Neon Nitrogen Air Fluorine Argon Oxygen Methane
Normal boiling point, K 4.2 20.4 27.1 77.3 78.9 85.3 87.3 90.2 111.7
Critical temperature, K 5.2 33.2 44.4 126.1 133.3 118.2 150.7 154.6 190.7
Critical pressure, MPa 0.23 1.31 2.71 3.38 3.90 5.55 4.87 5.06 4.63
Temperature at triple point, K b 13.9 19.0 63.2 — 53.5 83.8 54.4 88.7
Pressure at triple point, MPa × 10 3 c 7.2 43.0 12.8 — 0.22 68.6 0.15 10.1
Density, kg/m 3 124.9 70.9 1204 810.8 874.0 1505 1403 1134 425.0
Heat of vaporization, kJ/kg 20.7 446.3 86.6 198.4 205.1 166.5 161.6 213.1 509.7
Specific heat, kJ/kg · K 4.56 9.78 1.84 2.04 1.97 1.55 1.14 1.70 3.45
Viscosity, (kg/m · sec) × 10 6 3.57 13.06 124.0 157.9 80.6 244.7 252.1 188.0 118.6
Thermal conductivity, 0.027 0.118 0.130 0.139 — 0.135 0.123 0.148 0.111
(kJ/m · sec · K) × 10 3
Dielectric constant 1.0492 1.226 — 1.434 — 1.43 1.52 1.4837 1.6758
a
Equilibrium hydrogen.
b
λ-Point temperature, 2.17 K.
c −3
λ-Point pressure, 5.02 × 10 MPa.
that the user may program the formulations in any ap- pressure of 2.5 MPa or more even to exist as a solid below
propriate computer language or format consistent with a temperature of 3 K.
a particular application. Selected property data for some Other properties of helium-4 show similar surprises.
common cryogens are presented in Table I. Unique prop- At the λ point, the specific heat of the liquid increases
erties of several of these cryogens are noted below. to a large value as the temperature is decreased through
Liquid helium-4 has some very unusual properties since this point. Once below the λ point, the specific heat of he-
it can exist in two different liquid phases, namely, liquid lium II rapidly decreases to zero. The thermal conductivity
heliumIandliquidheliumII(Fig.1).Theformerislabeled of helium I, on the other hand, decreases with decreasing
the normal fluid, while the latter has been designated the temperature. However, once the transition to helium II has
superfluid since under certain conditions the fluid acts as been made, the thermal conductivity of the liquid can in-
6
if it had no viscosity. The phase transition between the crease in value by as much as 10 that of helium I.
two liquid phases is identified as the λ line. Intersection A unique property of hydrogen is that it can exist in
of the latter with the vapor-pressure curve is known as two different molecular forms, namely, orthohydrogen
the λ point. Helium-4 has no triple point and requires a and parahydrogen. The ortho and para forms differ in
the relative orientation of the nuclear spins of the two
atoms associated with the diatomic molecule. The ther-
modynamic equilibrium composition of the ortho and para
varieties is temperature dependent. At ambient tempera-
tures, the equilibrium mixture is 75% orthohydrogen and
25% parahydrogen and is designated as normal hydro-
gen. With decreasing temperatures, the thermodynamic
equilibrium shifts to essentially 100% parahydrogen at
20.4 K. the normal boiling point of hydrogen. The con-
version from normal hydrogen to parahydrogen is exother-
mic and evolves sufficient energy to vaporize ∼1% of the
stored liquid per hour. To minimize such losses in the
commercial production of liquid hydrogen, a catalyst is
used to effect the conversion from normal hydrogen to
the thermodynamic equilibrium concentration during the
liquefaction process.
Thetwoformsofhydrogenhavedifferentspecificheats.
This difference, in turn, affects other thermal and transport
FIGURE 1 Phase diagram for helium-4. properties of hydrogen. For example, parahydrogen gas