Page 197 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Chemical Engineering
P. 197
P1: GAE/LSK P2: FLV Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN004D-ID159 June 8, 2001 15:47
94 Crystallization Processes
TABLE I Water of Hydration for MgSO 4
Form Name wt% MgSO 4 Conditions
◦
MgSO 4 Anhydrous magnesium sulfate 0.0 >100 C
◦
MgSO 4 ·H 2 O Magnesium sulfate monohydrate 87.0 67 to 100 C
◦
MgSO 4 ·6H 2 O Magnesium sulfate hexahydrate 52.7 48 to 67 C
◦
MgSO 4 ·7H 2 O Magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 48.8 2 to 48 C
◦
MgSO 4 ·12 H 2 O Magnesium sulfate dodecahydrate 35.8 −4to2 C
but (2) cooling a saturated sodium chloride solution ac- sion of the complex solubility behavior in such systems
complishes little crystallization, and vaporization of water by graphical means usually is limited to systems of two
is required to increase the yield. solutes. The interaction of added solutes on solubility is
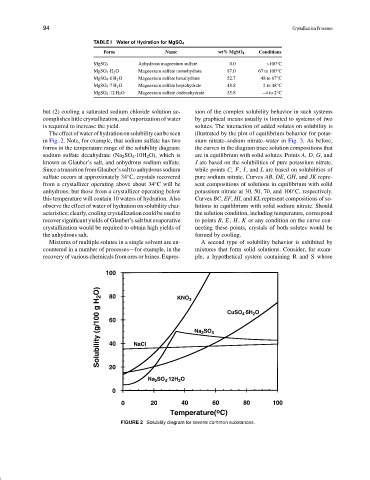
Theeffectofwaterofhydrationonsolubilitycanbeseen illustrated by the plot of equilibrium behavior for potas-
in Fig. 2. Note, for example, that sodium sulfate has two sium nitrate–sodium nitrate–water in Fig. 3. As before,
forms in the temperature range of the solubility diagram: the curves in the diagram trace solution compositions that
sodium sulfate decahydrate (Na 2 SO 4 ·10H 2 O), which is are in equilibrium with solid solutes. Points A, D, G, and
known as Glauber’s salt, and anhydrous sodium sulfate. J are based on the solubilities of pure potassium nitrate,
Since a transition from Glauber’s salt to anhydrous sodium while points C, F, I, and L are based on solubilities of
◦
sulfate occurs at approximately 34 C, crystals recovered pure sodium nitrate. Curves AB, DE, GH, and JK repre-
from a crystallizer operating above about 34 C will be sent compositions of solutions in equilibrium with solid
◦
anhydrous, but those from a crystallizer operating below potassium nitrate at 30, 50, 70, and 100 C, respectively.
◦
this temperature will contain 10 waters of hydration. Also Curves BC, EF, HI, and KL represent compositions of so-
observe the effect of water of hydration on solubility char- lutions in equilibrium with solid sodium nitrate. Should
acteristics; clearly, cooling crystallization could be used to the solution condition, including temperature, correspond
recover significant yields of Glauber’s salt but evaporative to points B, E, H, K or any condition on the curve con-
crystallization would be required to obtain high yields of necting these points, crystals of both solutes would be
the anhydrous salt. formed by cooling.
Mixtures of multiple solutes in a single solvent are en- A second type of solubility behavior is exhibited by
countered in a number of processes—for example, in the mixtures that form solid solutions. Consider, for exam-
recovery of various chemicals from ores or brines. Expres- ple, a hypothetical system containing R and S whose
FIGURE 2 Solubility diagram for several common substances.