Page 117 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 117
P1: FPP Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-85 May 17, 2001 20:35
Catalysis, Homogeneous 465
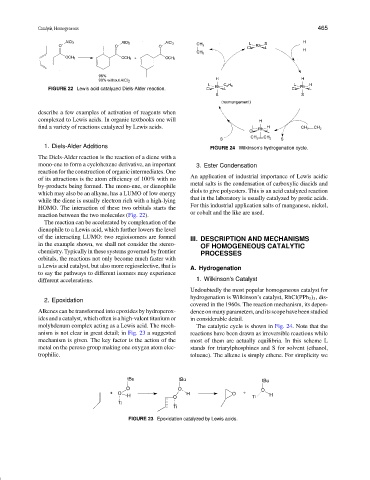
FIGURE 22 Lewis acid catalyzed Diels-Alder reaction.
describe a few examples of activation of reagents when
complexed to Lewis acids. In organic textbooks one will
find a variety of reactions catalyzed by Lewis acids.
1. Diels-Alder Additions FIGURE 24 Wilkinson’s hydrogenation cycle.
The Diels-Alder reaction is the reaction of a diene with a
mono-ene to form a cyclohexene derivative, an important 3. Ester Condensation
reaction for the construction of organic intermediates. One
An application of industrial importance of Lewis acidic
of its attractions is the atom efficiency of 100% with no
metal salts is the condensation of carboxylic diacids and
by-products being formed. The mono-ene, or dienophile
diols to give polyesters. This is an acid catalyzed reaction
which may also be an alkyne, has a LUMO of low energy
that in the laboratory is usually catalyzed by protic acids.
while the diene is usually electron rich with a high-lying
For this industrial application salts of manganese, nickel,
HOMO. The interaction of these two orbitals starts the
or cobalt and the like are used.
reaction between the two molecules (Fig. 22).
The reaction can be accelerated by complexation of the
dienophile to a Lewis acid, which further lowers the level
of the interacting LUMO: two regioisomers are formed III. DESCRIPTION AND MECHANISMS
in the example shown, we shall not consider the stereo- OF HOMOGENEOUS CATALYTIC
chemistry. Typically in these systems governed by frontier PROCESSES
orbitals, the reactions not only become much faster with
a Lewis acid catalyst, but also more regioselective, that is
A. Hydrogenation
to say the pathways to different isomers may experience
different accelerations. 1. Wilkinson’s Catalyst
Undoubtedly the most popular homogeneous catalyst for
hydrogenation is Wilkinson’s catalyst, RhCl(PPh 3 ) 3 , dis-
2. Epoxidation
covered in the 1960s. The reaction mechanism, its depen-
Alkenes can be transformed into epoxides by hydroperox- denceonmanyparameters,anditsscopehavebeenstudied
ides and a catalyst, which often is a high-valent titanium or in considerable detail.
molybdenum complex acting as a Lewis acid. The mech- The catalytic cycle is shown in Fig. 24. Note that the
anism is not clear in great detail; in Fig. 23 a suggested reactions have been drawn as irreversible reactions while
mechanism is given. The key factor is the action of the most of them are actually equilibria. In this scheme L
metal on the peroxo group making one oxygen atom elec- stands for triarylphosphines and S for solvent (ethanol,
trophilic. toluene). The alkene is simply ethene. For simplicity we
FIGURE 23 Epoxidation catalyzed by Lewis acids.