Page 42 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 42
P1: LDK Revised Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN001F-21 May 7, 2001 13:44
Alkaloids 481
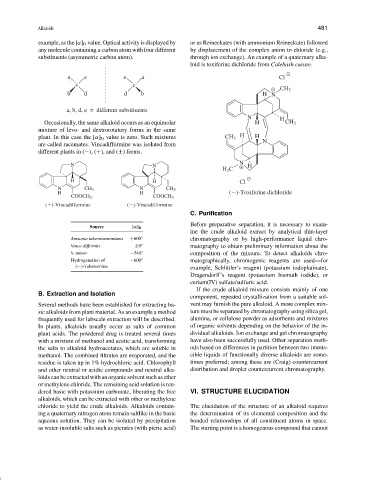
example, as the [α] D value. Optical activity is displayed by or as Reineckates (with ammonium Reineckate) followed
any molecule containing a carbon atom with four different by displacement of the complex anion to chloride (e.g.,
substituents (asymmetric carbon atom). through ion exchange). An example of a quaternary alka-
loid is toxiferine dichloride from Calebash curare.
a e e a Cl
c c
CH 3
b d d b H N
a, b, d, e = different substituents
N H
Occasionally, the same alkaloid occurs as an equimolar H CH 3
mixture of levo- and dextrorotatory forms in the same
plant. In this case the [α] D value is zero. Such mixtures CH 3 H H
N
are called racemates. Vincadifformine was isolated from
different plants in (−), (+), and (±) forms.
N N N H
H 3 C
H H Cl
N CH 3 N CH 3
H H ( )-Toxiferine dichloride
COOCH 3 COOCH 3
( )-Vincadifformine ( )-Vincadifformine
C. Purification
Before preparative separation, it is necessary to exam-
Source [α] D
ine the crude alkaloid extract by analytical thin-layer
Amsonia tabernaemontana +600 ◦ chromatography or by high-performance liquid chro-
Vinca difformis ±0 ◦ matography to obtain preliminary information about the
V. minor −540 ◦ composition of the mixture. To detect alkaloids chro-
Hydrogenation of −600 ◦ matographically, chromogenic reagents are used—for
(−)-Tabersonine example, Schlittler’s reagent (potassium iodoplatinate),
Dragendorff’s reagent (potassium bismuth iodide), or
cerium(IV) sulfate/sulfuric acid.
If the crude alkaloid mixture consists mainly of one
B. Extraction and Isolation
component, repeated crystallization from a suitable sol-
Several methods have been established for extracting ba- vent may furnish the pure alkaloid. A more complex mix-
sic alkaloids from plant material. As an example a method ture must be separated by chromatography using silica gel,
frequently used for labscale extraction will be described. alumina, or cellulose powder as adsorbents and mixtures
In plants, alkaloids usually occur as salts of common of organic solvents depending on the behavior of the in-
plant acids. The powdered drug is treated several times dividual alkaloids. Ion exchange and gel chromatography
with a mixture of methanol and acetic acid, transforming have also been successfully used. Other separation meth-
the salts to alkaloid hydroacetates, which are soluble in ods based on differences in partition between two immis-
methanol. The combined filtrates are evaporated, and the cible liquids of functionally diverse alkaloids are some-
residue is taken up in 1% hydrochloric acid. Chlorophyll times preferred; among these are (Craig) countercurrent
and other neutral or acidic compounds and neutral alka- distribution and droplet countercurrent chromatography.
loids can be extracted with an organic solvent such as ether
or methylene chloride. The remaining acid solution is ren-
dered basic with potassium carbonate, liberating the free VI. STRUCTURE ELUCIDATION
alkaloids, which can be extracted with other or methylene
chloride to yield the crude alkaloids. Alkaloids contain- The elucidation of the structure of an alkaloid requires
ing a quaternary nitrogen atom remain saltlike in the basic the determination of its elemental composition and the
aqueous solution. They can be isolated by precipitation bonded relationships of all constituent atoms in space.
as water-insoluble salts such as picrates (with picric acid) The starting point is a homogenous compound that cannot