Page 76 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 76
P1: LLL/LLL P2: FJU Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-80 May 25, 2001 20:18
384 Carbohydrates
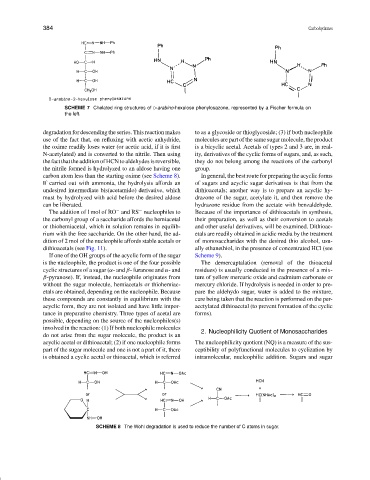
SCHEME 7 Chelated ring structures of D-arabino-hexulose phenylosazone, represented by a Fischer formula on
the left.
degradation for descending the series. This reaction makes to as a glycoside or thioglycoside; (3) if both nucleophile
use of the fact that, on refluxing with acetic anhydride, molecules are part of the same sugar molecule, the product
the oxime readily loses water (or acetic acid, if it is first is a bicyclic acetal. Acetals of types 2 and 3 are, in real-
N-acetylated) and is converted to the nitrile. Then using ity, derivatives of the cyclic forms of sugars, and, as such,
the fact that the addition of HCN to aldehydes is reversible, they do not belong among the reactions of the carbonyl
the nitrile formed is hydrolyzed to an aldose having one group.
carbon atom less than the starting oxime (see Scheme 8). In general, the best route for preparing the acyclic forms
If carried out with ammonia, the hydrolysis affords an of sugars and acyclic sugar derivatives is that from the
undesired intermediate bis(acetamido) derivative, which dithioacetals; another way is to prepare an acyclic hy-
must by hydrolyzed with acid before the desired aldose drazone of the sugar, acetylate it, and then remove the
can be liberated. hydrazone residue from the acetate with benzaldehyde.
The addition of l mol of RO and RS nucleophiles to Because of the importance of dithioacetals in synthesis,
−
−
the carbonyl group of a saccharide affords the hemiacetal their preparation, as well as their conversion to acetals
or thiohemiacetal, which in solution remains in equilib- and other useful derivatives, will be examined. Dithioac-
rium with the free saccharide. On the other hand, the ad- etals are readily obtained in acidic media by the treatment
dition of 2 mol of the nucleophile affords stable acetals or of monosaccharides with the desired thio alcohol, usu-
dithioacetals (see Fig. 11). ally ethanethiol, in the presence of concentrated HCl (see
If one of the OH groups of the acyclic form of the sugar Scheme 9).
is the nucleophile, the product is one of the four possible The demercaptalation (removal of the thioacetal
cyclic structures of a sugar (α- and β- furanose and α- and residues) is usually conducted in the presence of a mix-
β-pyranose). If, instead, the nucleophile originates from ture of yellow mercuric oxide and cadmium carbonate or
without the sugar molecule, hemiacetals or thiohemiac- mercury chloride. If hydrolysis is needed in order to pre-
etals are obtained, depending on the nucleophile. Because pare the aldehydo sugar, water is added to the mixture,
these compounds are constantly in equilibrium with the care being taken that the reaction is performed on the per-
acyclic form, they are not isolated and have little impor- acetylated dithioacetal (to prevent formation of the cyclic
tance in preparative chemistry. Three types of acetal are forms).
possible, depending on the source of the nucleophiles(s)
involved in the reaction: (1) If both nucleophile molecules
2. Nucleophilicity Quotient of Monosaccharides
do not arise from the sugar molecule, the product is an
acyclic acetal or dithioacetal; (2) if one nucleophile forms The nucleophilicity quotient (NQ) is a measure of the sus-
part of the sugar molecule and one is not a part of it, there ceptibility of polyfunctional molecules to cyclization by
is obtained a cyclic acetal or thioacetal, which is referred intramolecular, nucleophilic addition. Sugars and sugar
SCHEME 8 The Wohl degradation is used to reduce the number of C atoms in sugar.