Page 71 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Organic Chemistry
P. 71
P1: LLL/LLL P2: FJU Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN002C-80 May 25, 2001 20:18
Carbohydrates 379
TABLE V Free Energy of Unfavorable
Interactions
Type of interaction Free energy (kJ)
Gauche-1,2
O-1-e-O-e 2.30
O-1-e-O-a 4.19
O-e-O-e or -a 1.47
C-e-O-e or -a 1.88
Axial–axial-1.3
O–O 6.28
O–C 10.47
O–H 1.88
C–H 3.77
Anomeric effect 1.26
however, play an important role during glycoside forma-
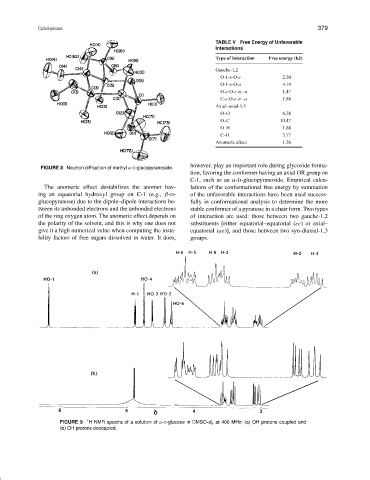
FIGURE 8 Neutron diffraction of methyl α-D-glucopyranoside.
tion, favoring the conformer having an axial OR group on
C-1, such as an α-D-glucopyranoside. Empirical calcu-
The anomeric effect destabilizes the anomer hav- lations of the conformational free energy by summation
ing an equatorial hydroxyl group on C-1 (e.g., β-D- of the unfavorable interactions have been used success-
glucopyranose) due to the dipole–dipole interactions be- fully in conformational analysis to determine the more
tween its unbonded electrons and the unbonded electrons stable conformer of a pyranose in a chair form. Two types
of the ring oxygen atom. The anomeric effect depends on of interaction are used: those between two gauche-1,2
the polarity of the solvent, and this is why one does not substituents [either equatorial–equatorial (ee) or axial–
give it a high numerical value when computing the insta- equatorial (ae)], and those between two syn-diaxial-1,3
bility factors of free sugars dissolved in water. It does, groups.
FIGURE 9 1 H NMR spectra of a solution of α-D-glucose in DMSO-d 6 at 400 MHz: (a) OH protons coupled and
(b) OH protons decoupled.