Page 166 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 166
P1: GQT Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006F-275 June 29, 2001 21:12
Gas Chromatography 457
column, at which the crucial physicochemical processes stationary phase, the individual sample components even-
of the actual compound separation occur. tually form their own concentration bands, which reach
The separation column contains the stationary phase, the column’s end at different times. A detector is situated
while the mobile phase (frequently referred to as the car- at the column’s end to sense and quantitatively measure
rier gas) is permitted to flow through this column from a the relative amounts of these sample components.
pressurized gas cylinder (source of the mobile phase). The The detector, together with auxiliary electronic and
rate of mobile-phase delivery is controlled by a pressure recording devices, is instrumental in generating the chro-
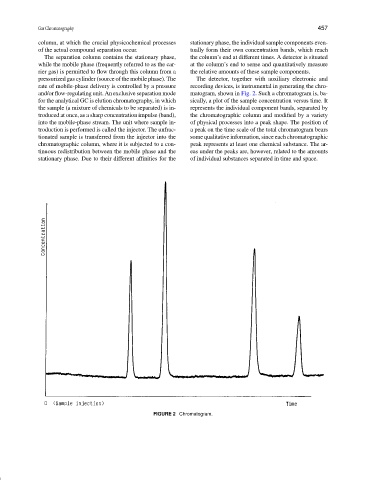
and/or flow-regulating unit. An exclusive separation mode matogram, shown in Fig. 2. Such a chromatogram is, ba-
for the analytical GC is elution chromatography, in which sically, a plot of the sample concentration versus time. It
the sample (a mixture of chemicals to be separated) is in- represents the individual component bands, separated by
troduced at once, as a sharp concentration impulse (band), the chromatographic column and modified by a variety
into the mobile-phase stream. The unit where sample in- of physical processes into a peak shape. The position of
troduction is performed is called the injector. The unfrac- a peak on the time scale of the total chromatogram bears
tionated sample is transferred from the injector into the some qualitative information, since each chromatographic
chromatographic column, where it is subjected to a con- peak represents at least one chemical substance. The ar-
tinuous redistribution between the mobile phase and the eas under the peaks are, however, related to the amounts
stationary phase. Due to their different affinities for the of individual substances separated in time and space.
FIGURE 2 Chromatogram.