Page 171 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 171
P1: GQT Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006F-275 June 29, 2001 21:12
462 Gas Chromatography
they are effectively blocked (deactivated) by a silylation
reaction, an example of which is given below:
Si OH Si O CH 3
H 3 C Cl
O + Si -2HCl O Si
H 3 C Cl
Si OH Si O CH 3
(a part of original (dimethyldichlorosilane. (deactivated surface)
surface structure) a deactivation agent)
The solid support is subsequently impregnated by a liq-
uid stationary phase. While many solid supports can carry
up to 25% by weight of a liquid phase before becoming
visibly wet, much lower phase loadings (a few percent)
are used in practice. Both the amount and the chemical
type of a stationary phase are crucial to the separation
characteristics (efficiency and sample capacity) of a chro-
matographic column. Packed columns are considered to
be low-efficiency, high-capacity GC columns. While their
best efficiencies amount to no more than a few thousand
theoretical plates, packed columns can tolerate microgram
amounts of samples. Only carefully and totally packed
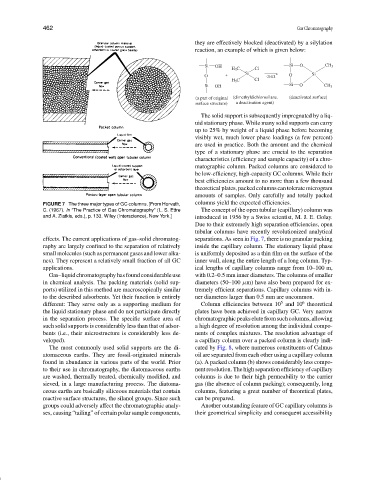
FIGURE 7 The three major types of GC columns. [From Horvath, columns yield the expected efficiencies.
C. (1967). In “The Practice of Gas Chromatography” (L. S. Ettre The concept of the open tubular (capillary) column was
and A. Zlatkis, eds.), p. 133. Wiley (Interscience), New York.] introduced in 1956 by a Swiss scientist, M. J. E. Golay.
Due to their extremely high separation efficiencies, open
tubular columns have recently revolutionized analytical
effects. The current applications of gas–solid chromatog- separations. As seen in Fig. 7, there is no granular packing
raphy are largely confined to the separation of relatively inside the capillary column. The stationary liquid phase
small molecules (such as permanent gases and lower alka- is uniformly deposited as a thin film on the surface of the
nes). They represent a relatively small fraction of all GC inner wall, along the entire length of a long column. Typ-
applications. ical lengths of capillary columns range from 10–100 m,
Gas–liquid chromatography has found considerable use with 0.2–0.5 mm inner diameters. The columns of smaller
in chemical analysis. The packing materials (solid sup- diameters (50–100 µm) have also been prepared for ex-
ports) utilized in this method are macroscopically similar tremely efficient separations. Capillary columns with in-
to the described adsorbents. Yet their function is entirely ner diameters larger than 0.5 mm are uncommon.
6
5
different: They serve only as a supporting medium for Column efficiencies between 10 and 10 theoretical
the liquid stationary phase and do not participate directly plates have been achieved in capillary GC. Very narrow
in the separation process. The specific surface area of chromatographic peaks elute from such columns, allowing
such solid supports is considerably less than that of adsor- a high degree of resolution among the individual compo-
bents (i.e., their microstructure is considerably less de- nents of complex mixtures. The resolution advantage of
veloped). a capillary column over a packed column is clearly indi-
The most commonly used solid supports are the di- cated by Fig. 8, where numerous constituents of Calmus
atomaceous earths. They are fossil-originated minerals oil are separated from each other using a capillary column
found in abundance in various parts of the world. Prior (a). A packed column (b) shows considerably less compo-
to their use in chromatography, the diatomaceous earths nent resolution. The high separation efficiency of capillary
are washed, thermally treated, chemically modified, and columns is due to their high permeability to the carrier
sieved, in a large manufacturing process. The diatoma- gas (the absence of column packing); consequently, long
ceous earths are basically siliceous materials that contain columns, featuring a great number of theoretical plates,
reactive surface structures, the silanol groups. Since such can be prepared.
groups could adversely affect the chromatographic analy- Another outstanding feature of GC capillary columns is
ses, causing “tailing” of certain polar sample components, their geometrical simplicity and consequent accessibility