Page 273 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 273
P1: GSR/GLE P2: FXY Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009G-958 July 18, 2001 0:57
Mass Spectrometry in Forensic Science 161
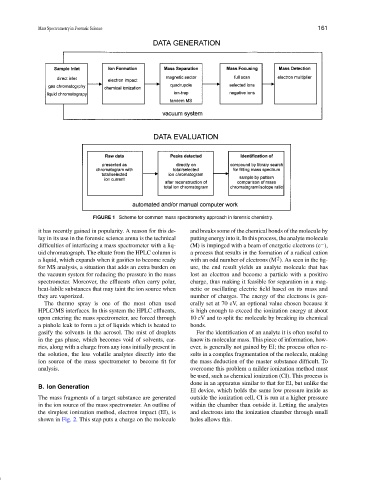
FIGURE 1 Scheme for common mass spectrometry approach in forensic chemistry.
it has recently gained in popularity. A reason for this de- and breaks some of the chemical bonds of the molecule by
lay in its use in the forensic science arena is the technical putting energy into it. In this process, the analyte molecule
−
difficulties of interfacing a mass spectrometer with a liq- (M) is impinged with a beam of energetic electrons (e ),
uid chromatograph. The eluate from the HPLC column is a process that results in the formation of a radical cation
+
a liquid, which expands when it gasifies to become ready with an odd number of electrons (M ). As seen in the fig-
✉
for MS analysis, a situation that adds an extra burden on ure, the end result yields an analyte molecule that has
the vacuum system for reducing the pressure in the mass lost an electron and become a particle with a positive
spectrometer. Moreover, the effluents often carry polar, charge, thus making it feasible for separation in a mag-
heat-labile substances that may taint the ion source when netic or oscillating electric field based on its mass and
they are vaporized. number of charges. The energy of the electrons is gen-
The thermo spray is one of the most often used erally set at 70 eV, an optional value chosen because it
HPLC/MS interfaces. In this system the HPLC effluents, is high enough to exceed the ionization energy at about
upon entering the mass spectrometer, are forced through 10 eV and to split the molecule by breaking its chemical
a pinhole leak to form a jet of liquids which is heated to bonds.
gasify the solvents in the aerosol. The mist of droplets For the identification of an analyte it is often useful to
in the gas phase, which becomes void of solvents, car- know its molecular mass. This piece of information, how-
ries, along with a charge from any ions initially present in ever, is generally not gained by EI; the process often re-
the solution, the less volatile analytes directly into the sults in a complex fragmentation of the molecule, making
ion source of the mass spectrometer to become fit for the mass deduction of the master substance difficult. To
analysis. overcome this problem a milder ionization method must
be used, such as chemical ionization (CI). This process is
done in an apparatus similar to that for EI, but unlike the
B. Ion Generation
EI device, which holds the same low pressure inside as
The mass fragments of a target substance are generated outside the ionization cell, CI is run at a higher pressure
in the ion source of the mass spectrometer. An outline of within the chamber than outside it. Letting the analytes
the simplest ionization method, electron impact (EI), is and electrons into the ionization chamber through small
shown in Fig. 2. This step puts a charge on the molecule holes allows this.