Page 278 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd Analytical Chemistry
P. 278
P1: GSR/GLE P2: FXY Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN009G-958 July 18, 2001 0:57
166 Mass Spectrometry in Forensic Science
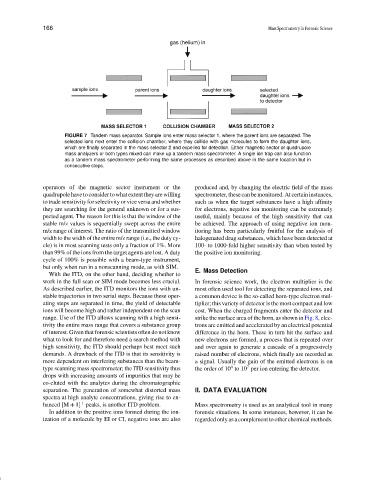
FIGURE 7 Tandem mass separator. Sample ions enter mass selector 1, where the parent ions are separated. The
selected ions next enter the collision chamber, where they collide with gas molecules to form the daughter ions,
which are finally separated in the mass selector 2 and expelled for detection. Either magnetic sector or quadrupole
mass analyzers or both types mixed can make up a tandem mass spectrometer. A single ion trap can also function
as a tandem mass spectrometer performing the same processes as described above in the same location but in
consecutive steps.
operators of the magnetic sector instrument or the produced and, by changing the electric field of the mass
quadrupole have to consider to what extent they are willing spectrometer,thesecanbemonitored.Atcertaininstances,
to trade sensitivity for selectivity or vice versa and whether such as when the target substances have a high affinity
they are searching for the general unknown or for a sus- for electrons, negative ion monitoring can be extremely
pected agent. The reason for this is that the window of the useful, mainly because of the high sensitivity that can
stable m/z values is sequentially swept across the entire be achieved. The approach of using negative ion mon-
m/z range of interest. The ratio of the transmitted window itoring has been particularly fruitful for the analysis of
width to the width of the entire m/z range (i.e., the duty cy- halogenated drug substances, which have been detected at
cle) is in most scanning tests only a fraction of 1%. More 100- to 1000-fold higher sensitivity than when tested by
than 99% of the ions from the target agents are lost. A duty the positive ion monitoring.
cycle of 100% is possible with a beam-type instrument,
but only when run in a nonscanning mode, as with SIM.
E. Mass Detection
With the ITD, on the other hand, deciding whether to
work in the full scan or SIM mode becomes less crucial. In forensic science work, the electron multiplier is the
As described earlier, the ITD monitors the ions with un- most often used tool for detecting the separated ions, and
stable trajectories in two serial steps. Because these oper- a common device is the so-called horn-type electron mul-
ating steps are separated in time, the yield of detectable tiplier; this variety of detector is the most compact and low
ions will become high and rather independent on the scan cost. When the charged fragments enter the detector and
range. Use of the ITD allows scanning with a high sensi- strike the surface area of the horn, as shown in Fig. 8, elec-
tivity the entire mass range that covers a substance group trons are emitted and accelerated by an electrical potential
of interest. Given that forensic scientists often do not know difference in the horn. These in turn hit the surface and
what to look for and therefore need a search method with new electrons are formed, a process that is repeated over
high sensitivity, the ITD should perhaps best meet such and over again to generate a cascade of a progressively
demands. A drawback of the ITD is that its sensitivity is raised number of electrons, which finally are recorded as
more dependent on interfering substances than the beam- a signal. Usually the gain of the emitted electrons is on
7
4
type scanning mass spectrometer; the ITD sensitivity thus the order of 10 to 10 per ion entering the detector.
drops with increasing amounts of impurities that may be
co-eluted with the analytes during the chromatographic
separation. The generation of somewhat distorted mass II. DATA EVALUATION
spectra at high analyte concentrations, giving rise to en-
hanced [M + 1] peaks, is another ITD problem. Mass spectrometry is used as an analytical tool in many
+
In addition to the positive ions formed during the ion- forensic situations. In some instances, however, it can be
ization of a molecule by EI or CI, negative ions are also regarded only as a complement to other chemical methods.