Page 168 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 168
P1: GPAFinal Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013D-616 July 27, 2001 12:5
208 Protein Structure
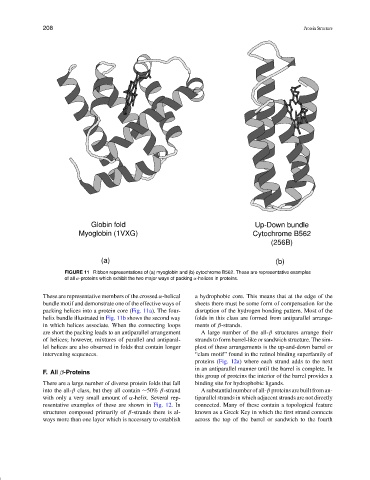
Globin fold Up-Down bundle
Myoglobin (1VXG) Cytochrome B562
(256B)
(a) (b)
FIGURE 11 Ribbon representations of (a) myoglobin and (b) cytochrome B562. These are representative examples
of all α-proteins which exhibit the two major ways of packing α-helices in proteins.
These are representative members of the crossed α-helical a hydrophobic core. This means that at the edge of the
bundle motif and demonstrate one of the effective ways of sheets there must be some form of compensation for the
packing helices into a protein core (Fig. 11a). The four- disruption of the hydrogen bonding pattern. Most of the
helix bundle illustrated in Fig. 11b shows the second way folds in this class are formed from antiparallel arrange-
in which helices associate. When the connecting loops ments of β-strands.
are short the packing leads to an antiparallel arrangement A large number of the all-β structures arrange their
of helices; however, mixtures of parallel and antiparal- strands to form barrel-like or sandwich structure. The sim-
lel helices are also observed in folds that contain longer plest of these arrangements is the up-and-down barrel or
intervening sequences. “clam motif” found in the retinol binding superfamily of
proteins (Fig. 12a) where each strand adds to the next
in an antiparallel manner until the barrel is complete. In
F. All β-Proteins
this group of proteins the interior of the barrel provides a
There are a large number of diverse protein folds that fall binding site for hydrophobic ligands.
into the all-β class, but they all contain ∼50% β-strand A substantial number of all-β proteins are built from an-
with only a very small amount of α-helix. Several rep- tiparallel strands in which adjacent strands are not directly
resentative examples of these are shown in Fig. 12. In connected. Many of these contain a topological feature
structures composed primarily of β-strands there is al- known as a Greek Key in which the first strand connects
ways more than one layer which is necessary to establish across the top of the barrel or sandwich to the fourth