Page 170 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 170
P1: GPAFinal Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013D-616 July 27, 2001 12:5
210 Protein Structure
6
3 5
8
1 C 4
2 2 7
C
N N
(a) (b)
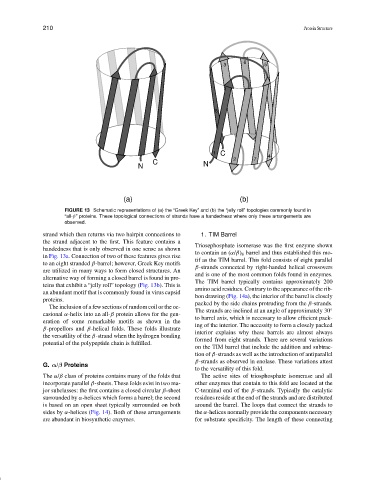
FIGURE 13 Schematic representations of (a) the “Greek Key” and (b) the “jelly roll” topologies commonly found in
“all-β” proteins. These topological connections of strands have a handedness where only these arrangements are
observed.
strand which then returns via two hairpin connections to 1. TIM Barrel
the strand adjacent to the first. This feature contains a
Triosephosphate isomerase was the first enzyme shown
handedness that is only observed in one sense as shown
to contain an (α/β) 8 barrel and thus established this mo-
in Fig. 13a. Connection of two of these features gives rise
tif as the TIM barrel. This fold consists of eight parallel
to an eight stranded β-barrel; however, Greek Key motifs
β-strands connected by right-handed helical crossovers
are utilized in many ways to form closed structures. An
and is one of the most common folds found in enzymes.
alternative way of forming a closed barrel is found in pro-
The TIM barrel typically contains approximately 200
teins that exhibit a “jelly roll” topology (Fig. 13b). This is
amino acid residues. Contrary to the appearance of the rib-
an abundant motif that is commonly found in virus capsid
bon drawing (Fig. 14a), the interior of the barrel is closely
proteins.
packed by the side chains protruding from the β-strands.
The inclusion of a few sections of random coil or the oc-
The strands are inclined at an angle of approximately 30 ◦
casional α-helix into an all-β protein allows for the gen-
to barrel axis, which is necessary to allow efficient pack-
eration of some remarkable motifs as shown in the
ing of the interior. The necessity to form a closely packed
β-propellors and β-helical folds. These folds illustrate
interior explains why these barrels are almost always
the versatility of the β-strand when the hydrogen bonding
formed from eight strands. There are several variations
potential of the polypeptide chain is fulfilled.
on the TIM barrel that include the addition and subtrac-
tion of β-strands as well as the introduction of antiparallel
β-strands as observed in enolase. These variations attest
G. α/β Proteins
to the versatility of this fold.
The α/β class of proteins contains many of the folds that The active sites of triosphosphate isomerase and all
incorporate parallel β-sheets. These folds exist in two ma- other enzymes that contain to this fold are located at the
jor subclasses: the first contains a closed circular β-sheet C-terminal end of the β-strands. Typically the catalytic
surrounded by α-helices which forms a barrel; the second residues reside at the end of the strands and are distributed
is based on an open sheet typically surrounded on both around the barrel. The loops that connect the strands to
sides by α-helices (Fig. 14). Both of these arrangements the α-helices normally provide the components necessary
are abundant in biosynthetic enzymes. for substrate specificity. The length of these connecting