Page 180 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 180
P1: GPB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013D-617 July 27, 2001 11:42
220 Protein Synthesis
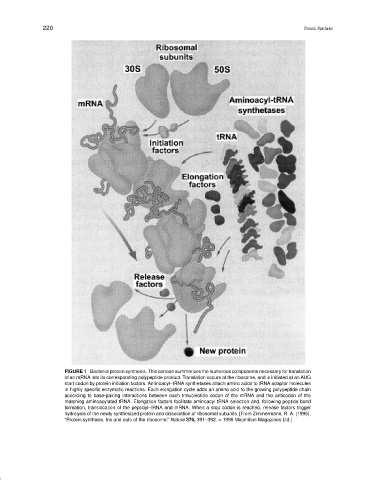
FIGURE 1 Bacterial protein synthesis. This cartoon summarizes the numerous components necessary for translation
of an mRNA into its corresponding polypeptide product. Translation occurs at the ribosome, and is initiated at an AUG
start codon by protein initiation factors. Aminoacyl–tRNA synthetases attach amino acids to tRNA adaptor molecules
in highly specific enzymatic reactions. Each elongation cycle adds an amino acid to the growing polypeptide chain
according to base-pairing interactions between each trinucleotide codon of the mRNA and the anticodon of the
matching aminoacylated tRNA. Elongation factors facilitate aminoacyl tRNA selection and, following peptide bond
formation, translocation of the peptidyl–tRNA and mRNA. When a stop codon is reached, release factors trigger
hydrolysis of the newly synthesized protein and dissociation of ribosomal subunits. [From Zimmermann, R. A. (1995).
“Protein synthesis. Ins and outs of the ribosome.” Nature 376, 391–392. C 1995 Macmillan Magazines Ltd.]