Page 178 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 178
P1: GPAFinal Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013D-616 July 27, 2001 12:5
218 Protein Structure
SEE ALSO THE FOLLOWING ARTICLES
BIOENERGETICS • HYDROGEN BOND • MACRO-
MOLECULES,STRUCTURE • MEMBRANE STRUCTURE •
NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE (NMR) • PROTEIN
FOLDING • PROTEIN SYNTHESIS • X-RAY ANALYSIS
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Branden, C., and Tooze, J. (1999). “Introduction to protein structure,”
(2nd edition), Garland.
Carter, C. W., Jr., Sweet, R. M., Abelson, J. N., and Simon, M. I.
(eds.) (1997). “Methods in Enzymology,” Volume 276, Macromolec-
ular Crystallography, Part A, Academic Press, New York.
Carter, C. W., Jr., Sweet, R. M., Abelson, J. N., and Simon, M. I.
(eds.) (1997). “Methods in Enzymology,” Volume 277, Macromolec-
ular Crystallography, Part B, Academic Press, New York.
Cavanagh, J., Palmer, A. G., III, Fairbrother, W., and Skelton N. (1996).
“ProteinNmrSpectroscopy:PrinciplesandPractice,”AcademicPress,
New York.
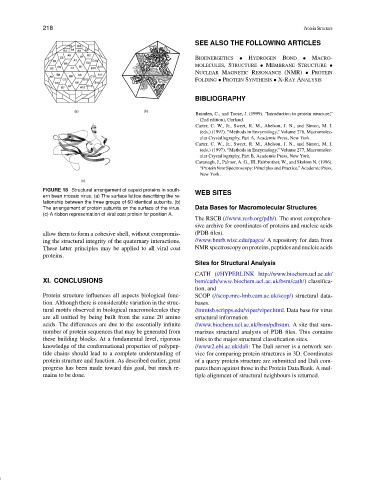
FIGURE 18 Structural arrangement of capsid proteins in south- WEB SITES
ern bean mosaic virus. (a) The surface lattice describing the re-
lationship between the three groups of 60 identical subunits. (b)
The arrangement of protein subunits on the surface of the virus. Data Bases for Macromolecular Structures
(c) A ribbon representation of viral coat protein for position A.
The RSCB (//www.rcsb.org/pdb/). The most comprehen-
sive archive for coordinates of proteins and nucleic acids
allow them to form a cohesive shell, without compromis- (PDB files).
ing the structural integrity of the quaternary interactions. //www.bmrb.wisc.edu/pages/ A repository for data from
These latter principles may be applied to all viral coat NMR spectroscopy on proteins, peptides and nucleic acids
proteins.
Sites for Structural Analysis
CATH (//HYPERLINK http://www.biochem.ucl.ac.uk/
XI. CONCLUSIONS bsm/cath/www.biochem.ucl.ac.uk/bsm/cath/) classifica-
tion, and
Protein structure influences all aspects biological func- SCOP (//scop.mrc-lmb.cam.ac.uk/scop/) structural data-
tion. Although there is considerable variation in the struc- bases.
tural motifs observed in biological macromolecules they //mmtsb.scripps.edu/viper/viper.html. Data base for virus
are all unified by being built from the same 20 amino structural information
acids. The differences are due to the essentially infinite //www.biochem.ucl.ac.uk/bsm/pdbsum. A site that sum-
number of protein sequences that may be generated from marizes structural analysis of PDB files. This contains
these building blocks. At a fundamental level, rigorous links to the major structural classification sites.
knowledge of the conformational properties of polypep- //www2.ebi.ac.uk/dali: The Dali server is a network ser-
tide chains should lead to a complete understanding of vice for comparing protein structures in 3D. Coordinates
protein structure and function. As described earlier, great of a query protein structure are submitted and Dali com-
progress has been made toward this goal, but much re- pares them against those in the Protein Data Bank. A mul-
mains to be done. tiple alignment of structural neighbours is returned.