Page 185 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 185
P1: GPB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013D-617 July 27, 2001 11:42
Protein Synthesis 225
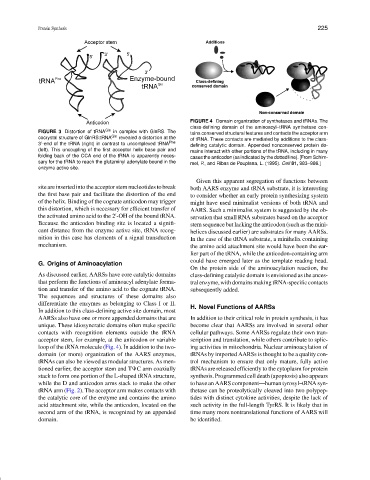
FIGURE 4 Domain organization of synthetases and tRNAs. The
class-defining domain of the aminoacyl–tRNA synthetase con-
FIGURE 3 Distortion of tRNA Gln in complex with GlnRS. The tains conserved structural features and contacts the acceptor arm
cocrystal structure of GlnRS:tRNA Gln revealed a distortion at the of tRNA. These contacts are mediated by additions to the class-
3 -end of the tRNA (right) in contrast to uncomplexed tRNA Phe defining catalytic domain. Appended nonconserved protein do-
(left). This uncoupling of the first acceptor helix base pair and mains interact with other portions of the tRNA, including in many
folding back of the CCA end of the tRNA is apparently neces- cases the anticodon (as indicated by the dotted line). [From Schim-
sary for the tRNA to reach the glutaminyl adenylate bound in the mel, P., and Ribas de Pouplana, L. (1995). Cell 81, 983–986.]
enzyme active site.
Given this apparent segregation of functions between
site are inserted into the acceptor stem nucleotides to break both AARS enzyme and tRNA substrate, it is interesting
the first base pair and facilitate the distortion of the end to consider whether an early protein synthesizing system
of the helix. Binding of the cognate anticodon may trigger might have used minimalist versions of both tRNA and
this distortion, which is necessary for efficient transfer of AARS. Such a minimalist system is suggested by the ob-
the activated amino acid to the 2 -OH of the bound tRNA. servation that small RNA substrates based on the acceptor
Because the anticodon binding site is located a signifi- stem sequence but lacking the anticodon (such as the mini-
cant distance from the enzyme active site, tRNA recog- helices discussed earlier) are substrates for many AARSs.
nition in this case has elements of a signal transduction In the case of the tRNA substrate, a minihelix containing
mechanism. the amino acid attachment site would have been the ear-
lier part of the tRNA, while the anticodon-containing arm
could have emerged later as the template reading head.
G. Origins of Aminoacylation
On the protein side of the aminoacylation reaction, the
As discussed earlier, AARSs have core catalytic domains class-defining catalytic domain is envisioned as the ances-
that perform the functions of aminoacyl adenylate forma- tral enzyme, with domains making tRNA-specific contacts
tion and transfer of the amino acid to the cognate tRNA. subsequently added.
The sequences and structures of these domains also
differentiate the enzymes as belonging to Class I or II.
H. Novel Functions of AARSs
In addition to this class-defining active site domain, most
AARSs also have one or more appended domains that are In addition to their critical role in protein synthesis, it has
unique. These idiosyncratic domains often make specific become clear that AARSs are involved in several other
contacts with recognition elements outside the tRNA cellular pathways. Some AARSs regulate their own tran-
acceptor stem, for example, at the anticodon or variable scription and translation, while others contribute to splic-
loop of the tRNA molecule (Fig. 4). In addition to the two- ing activities in mitochondria. Nuclear aminoacylation of
domain (or more) organization of the AARS enzymes, tRNAs by imported AARSs is thought to be a quality con-
tRNAs can also be viewed as modular structures. As men- trol mechanism to ensure that only mature, fully active
tioned earlier, the acceptor stem and T C arm coaxially tRNAs are released efficiently to the cytoplasm for protein
stack to form one portion of the L-shaped tRNA structure, synthesis. Programmed cell death (apoptosis) also appears
while the D and anticodon arms stack to make the other to have an AARS component—human tyrosyl–tRNA syn-
tRNA arm (Fig. 2). The acceptor arm makes contacts with thetase can be proteolytically cleaved into two polypep-
the catalytic core of the enzyme and contains the amino tides with distinct cytokine activities, despite the lack of
acid attachment site, while the anticodon, located on the such activity in the full-length TyrRS. It is likely that in
second arm of the tRNA, is recognized by an appended time many more nontranslational functions of AARS will
domain. be identified.