Page 188 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 188
P1: GPB Final Pages
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN013D-617 July 27, 2001 11:42
228 Protein Synthesis
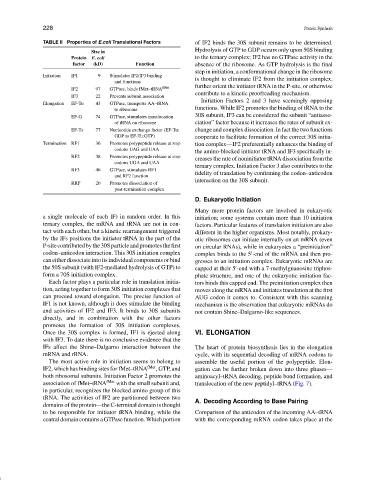
TABLE II Properties of E.coli Translational Factors of IF2 binds the 30S subunit remains to be determined.
Hydrolysis of GTP to GDP occurs only upon 50S binding
Size in
Protein E. coli to the ternary complex; IF2 has no GTPase activity in the
factor (kD) Function absence of the ribosome. As GTP hydrolysis is the final
step in initiation, a conformational change in the ribosome
Initiation IF1 9 Stimulates IF2/IF3 binding
is thought to eliminate IF2 from the initiation complex,
and functions
further orient the initiator tRNA in the P-site, or otherwise
IF2 97 GTPase, binds fMet–tRNA fMet
contribute to a kinetic proofreading mechanism.
IF3 22 Prevents subunit association
Initiation Factors 2 and 3 have seemingly opposing
Elongation EF-Tu 43 GTPase, transports AA–tRNA
functions. While IF2 promotes the binding of tRNA to the
to ribosome
30S subunit, IF3 can be considered the subunit “antiasso-
EF-G 74 GTPase, stimulates translocation
of tRNA on ribosome ciation” factor because it increases the rates of subunit ex-
EF-Ts 77 Nucleotide exchange factor (EF-Tu: change and complex dissociation. In fact the two functions
GDP to EF-Tu:GTP) cooperate to facilitate formation of the correct 30S initia-
Termination RF1 36 Promotes polypeptide release at stop tion complex—IF2 preferentially enhances the binding of
codons UAG and UAA
the amino-blocked initiator tRNA and IF3 specifically in-
RF2 38 Promotes polypeptide release at stop creases the rate of noninitiator tRNA dissociation from the
codons UGA and UAA
ternary complex. Initiation Factor 3 also contributes to the
RF3 46 GTPase, stimulates RF1
and RF2 function fidelity of translation by confirming the codon–anticodon
interaction on the 30S subunit.
RRF 20 Promotes dissociation of
post-termination complex
D. Eukaryotic Initiation
Many more protein factors are involved in eukaryotic
a single molecule of each IF) in random order. In this initiation; some systems contain more than 10 initiation
ternary complex, the mRNA and tRNA are not in con- factors. Particular features of translation initiation are also
tact with each other, but a kinetic rearrangement triggered different in the higher organisms. Most notably, prokary-
by the IFs positions the initiator tRNA in the part of the otic ribosomes can initiate internally on an mRNA (even
P-sitecontributedbythe30Sparticleandpromotesthefirst on circular RNAs), while in eukaryotes a “preinitiation”
codon–anticodon interaction. This 30S initiation complex complex binds to the 5 -end of the mRNA and then pro-
can either dissociate into its individual components or bind gresses to an initiation complex. Eukaryotic mRNAs are
the 50S subunit (with IF2-mediated hydrolysis of GTP) to capped at their 5 -end with a 7-methylguanosine triphos-
form a 70S initiation complex. phate structure, and one of the eukaryotic initiation fac-
Each factor plays a particular role in translation initia- tors binds this capped end. The preinitiation complex then
tion, acting together to form 30S initiation complexes that moves along the mRNA and initiates translation at the first
can proceed toward elongation. The precise function of AUG codon it comes to. Consistent with this scanning
IF1 is not known, although it does stimulate the binding mechanism is the observation that eukaryotic mRNAs do
and activities of IF2 and IF3. It binds to 30S subunits not contain Shine–Dalgarno-like sequences.
directly, and in combination with the other factors
promotes the formation of 30S initiation complexes.
Once the 30S complex is formed, IF1 is ejected along VI. ELONGATION
with IF3. To date there is no conclusive evidence that the
IFs affect the Shine–Dalgarno interaction between the The heart of protein biosynthesis lies in the elongation
mRNA and rRNA. cycle, with its sequential decoding of mRNA codons to
The most active role in initiation seems to belong to assemble the useful portion of the polypeptide. Elon-
IF2, which has binding sites for fMet–tRNA fMet , GTP, and gation can be further broken down into three phases—
both ribosomal subunits. Initiation Factor 2 promotes the aminoacyl–tRNA decoding, peptide bond formation, and
association of fMet–tRNA fMet with the small subunit and, translocation of the new peptidyl–tRNA (Fig. 7).
in particular, recognizes the blocked amino group of this
tRNA. The activities of IF2 are partitioned between two
A. Decoding According to Base Pairing
domains of the protein—the C-terminal domain is thought
to be responsible for initiator tRNA binding, while the Comparison of the anticodon of the incoming AA–tRNA
centraldomaincontainsaGTPasefunction.Whichportion with the corresponding mRNA codon takes place at the