Page 53 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 53
P1: GTQ Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006P-81 June 29, 2001 21:48
Glycoconjugates and Carbohydrates 837
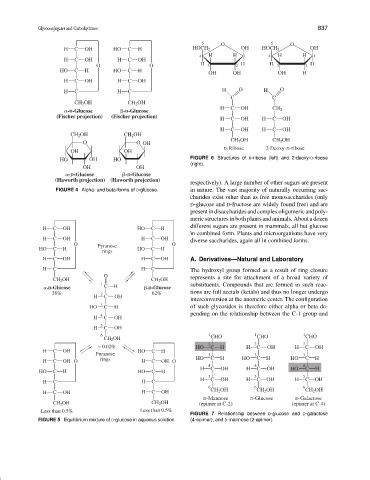
5 O 5 O
H C OH HO C H HOCH 2 OH HOCH 2 OH
4 H H 1 4 H H 1
H C OH H C OH
O O H 3 2 H H 3 2 H
HO C H HO C H
OH OH OH H
H C OH H C OH
H C H C H O H O
C C
CH 2 OH CH 2 OH
H C OH CH 2
-D-Glucose -D-Glucose
(Fischer projection) (Fischer projection)
H C OH H C OH
H C OH H C OH
CH 2 OH CH 2 OH
CH 2 OH CH 2 OH
O O OH
D-Ribose 2-Deoxy-D-ribose
OH OH
HO OH HO FIGURE 6 Structures of D-ribose (left) and 2-deoxy-D-ribose
(right).
OH OH
-D-Glucose -D-Glucose
(Haworth projection) (Haworth projection)
respectively). A large number of other sugars are present
FIGURE 4 Alpha- and beta-forms of D-glucose. in nature. The vast majority of naturally occurring sac-
charides exist other than as free monosaccharides (only
D-glucose and D-fructose are widely found free) and are
presentindisaccharidesandcomplexoligomericandpoly-
meric structures in both plants and animals. About a dozen
different sugars are present in mammals, all but glucose
H C OH HO C H
in combined form. Plants and microorganisms have very
H C OH H C OH diverse saccharides, again all in combined forms.
O Pyranose O
HO C H HO C H
rings
H C OH H C OH A. Derivatives—Natural and Laboratory
H C H C The hydroxyl group formed as a result of ring closure
O
CH 2 OH CH 2 OH represents a site for attachment of a broad variety of
1 substituents. Compounds that are formed in such reac-
-D-Glucose C H -D-Glucose
38% 2 62% tions are full acetals (ketals) and thus no longer undergo
H C OH
interconversion at the anomeric center. The configuration
3
HO C H of such glycosides is therefore either alpha or beta de-
pending on the relationship between the C-1 group and
4
H C OH
5
H C OH
6 1 CHO 1 CHO 1 CHO
CH 2 OH
~ 0.02% HO 2 C H H 2 C OH H 2 C OH
H C OH HO C H
Furanose 3 3 3
H C OH O rings H C OH O HO C H HO C H HO C H
4 4 4
H C OH H C OH HO C H
HO C H HO C H
5 5 5
H C OH H C OH H C OH
H C H C
6 6 6
H C OH H C OH CH 2 OH CH 2 OH CH 2 OH
D-Mannose D-Glucose D-Galactose
CH 2 OH CH 2 OH (epimer at C-2) (epimer at C-4)
Less than 0.5% Less than 0.5%
FIGURE 7 Relationship between D-glucose and D-galactose
FIGURE 5 Equilibrium mixture of D-glucose in aqueous solution. (4-epimer), and D-mannose (2-epimer).