Page 58 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 58
P1: GTQ Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006P-81 June 29, 2001 21:48
842 Glycoconjugates and Carbohydrates
6 CH 2 OH 6 CH 2 OH OH OH
HO 6 O
O O
5 5 4
HO H OH O O O
H H
4 OH H 1 O 4 OH H 1 O HO OH 1
3
H H H OH
3 2 3 2 ( 1 4)-linked D-glucose units
H OH H OH
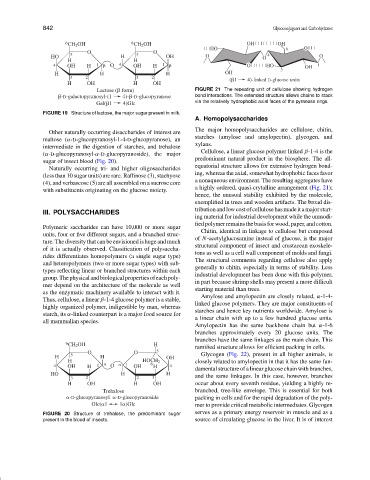
Lactose ( form) FIGURE 21 The repeating unit of cellulose showing hydrogen
-D-galactopyranosyl-(1 4)- -D-glucopyranose bond interactions. The extended structure allows chains to stack
Gal( 1 4)Glc via the relatively hydrophobic axial faces of the pyranose rings.
FIGURE 19 Structure of lactose, the major sugar present in milk.
A. Homopolysaccharides
The major homopolysaccharides are cellulose, chitin,
Other naturally occurring disaccharides of interest are
starches (amylose and amylopectin), glycogen, and
maltose (α-D-glucopyranosyl-1-4-D-glucopyranose), an
xylans.
intermediate in the digestion of starches, and trehalose
Cellulose, a linear glucose polymer linked β-1-4 is the
(α-D-glucopyranosyl-α-D-glucopyranoside), the major
predominant natural product in the biosphere. The all-
sugar of insect blood (Fig. 20).
equatorial structure allows for extensive hydrogen bond-
Naturally occurring tri- and higher oligosaccharides
ing, whereas the axial, somewhat hydrophobic faces favor
(less than 10 sugar units) are rare. Raffinose (3), stachyose
a nonaqueous environment. The resulting aggregates have
(4), and verbascose (5) are all assembled on a sucrose core
a highly ordered, quasi-crytalline arrangement (Fig. 21);
with substituents originating on the glucose moiety.
hence, the unusual stability exhibited by the molecule,
exemplified in trees and wooden artifacts. The broad dis-
tributionandlowcostofcellulosehasmadeitamajorstart-
III. POLYSACCHARIDES
ing material for industrial development while the unmodi-
fiedpolymerremainsthebasisforwood,paper,andcotton.
Polymeric saccharides can have 10,000 or more sugar
Chitin, identical in linkage to cellulose but composed
units, four or five different sugars, and a branched struc-
of N-acetylglucosamine instead of glucose, is the major
ture. The diversity that can be envisioned is huge and much
structural component of insect and crustacean exoskele-
of it is actually observed. Classification of polysaccha-
tons as well as a cell wall component of molds and fungi.
rides differentiates homopolymers (a single sugar type)
The structural comments regarding cellulose also apply
and heteropolymers (two or more sugar types) with sub-
generally to chitin, especially in terms of stability. Less
types reflecting linear or branched structures within each
industrial development has been done with this polymer,
group.Thephysicalandbiologicalpropertiesofeachpoly-
in part because shrimp shells may present a more difficult
mer depend on the architecture of the molecule as well
starting material than trees.
as the enzymatic machinery available to interact with it.
Amylose and amylopectin are closely related, α-1-4-
Thus, cellulose, a linear β-1-4 glucose polymer is a stable,
linked glucose polymers. They are major constituents of
highly organized polymer, indigestible by man, whereas
starches and hence key nutrients worldwide. Amylose is
starch, its α-linked counterpart is a major food source for
a linear chain with up to a few hundred glucose units.
all mammalian species.
Amylopectin has the same backbone chain but α-1-6
branches approximately every 20 glucose units. The
branches have the same linkages as the main chain. This
6 CH 2 OH H
ramified structure allows for efficient packing in cells.
O O 5
H 5 H OH Glycogen (Fig. 22), present in all higher animals, is
H HOCH 2 closely related to amylopectin in that it has the same fun-
4 OH H 1 O 1 OH 6 H 4
damental structure of a linear glucose chain with branches,
HO H H and the same linkages. In this case, however, branches
3 2 2 3
H OH H OH occur about every seventh residue, yielding a highly re-
Trehalose branched, tree-like envelope. This is essential for both
-D-glucopyranosyl -D-glucopyranoside packing in cells and for the rapid degradation of the poly-
Glc( 1 1 )Glc mer to provide critical metabolic intermediates. Glycogen
FIGURE 20 Structure of trehalose, the predominant sugar serves as a primary energy reservoir in muscle and as a
present in the blood of insects. source of circulating glucose in the liver. It is of interest