Page 59 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 59
P1: GTQ Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006P-81 June 29, 2001 21:48
Glycoconjugates and Carbohydrates 843
components necessitates, in many cases, that the saccha-
ride chain have a defined three-dimensional conformation.
Much work has been done to model the three-dimensional
structureofproteinsandmanyproteinstructureshavebeen
determined by X-ray crystallographic analysis. Much less
has been done with complex saccharides in terms of either
molecular dynamics or conformational analysis of larger
structures. The following discussion is intended to be rep-
3 units
6–7 units resentative only.
In addition to cellulose and xylan, plant cell walls con-
tain a variety of complex heteropolysaccharides including
6 CH 2 OH other glucans. Detailed structures have only been deter-
O mined for a limited number of these structures and their
H H
H interactions, possibly covalent, with other plant compo-
4 OH H 1 nents have rarely been determined in detail. Commercially
( 1 6)
O important are pectins, polygalcturonides, which are key
Branch branch
H OH point components of jellies and related uronides (gums) used
as thickening agents in a broad variety of applications
O
ranging from ice cream manufacture to the production
6
CH 2 of printing ink. Agars are galactans that are sulfated and
O also contain 3,6-anhydro-L-galactose, which have gelation
H H
H properties. They have broad application in microbiology.
4 OH H 1 Bacteria likewise produce a wide variety of complex,
O O cell-surface polysaccharides. Strains of Streptococcus
Main
Chain H OH pneumoniae, the causative agent of bacterial pneumonia,
are characterized by a capsular polysaccharide—more
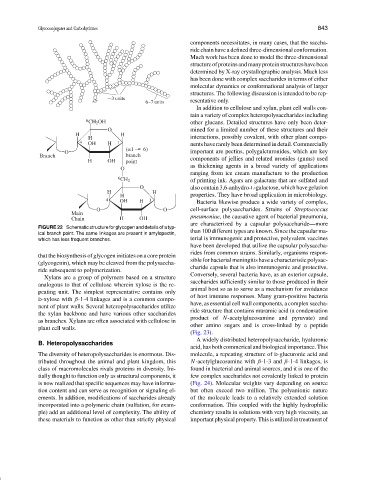
FIGURE 22 Schematic structure for glycogen and details of a typ-
ical branch point. The same linkages are present in amylopectin, than 100 different types are known. Since the capsular ma-
which has less frequent branches. terial is immunogenic and protective, polyvalent vaccines
have been developed that utilize the capsular polysaccha-
rides from common strains. Similarly, organisms respon-
that the biosynthesis of glycogen initiates on a core protein
sible for bacterial meningitis have a characteristic polysac-
(glycogenin), which may be cleaved from the polysaccha-
charide capsule that is also immunogenic and protective.
ride subsequent to polymerization.
Conversely, several bacteria have, as an exterior capsule,
Xylans are a group of polymers based on a structure
saccharides sufficiently similar to those produced in their
analogous to that of cellulose wherein xylose is the re-
animal host so as to serve as a mechanism for avoidance
peating unit. The simplest representative contains only
of host immune responses. Many gram-positive bacteria
D-xylose with β-1-4 linkages and is a common compo-
have, as essential cell wall components, a complex saccha-
nent of plant walls. Several heteropolysaccharides utilize
ride structure that contains muramic acid (a condensation
the xylan backbone and have various other saccharides
product of N-acetylglucosamine and pyruvate) and
as branches. Xylans are often associated with cellulose in
other amino sugars and is cross-linked by a peptide
plant cell walls.
(Fig. 23).
A widely distributed heteropolysaccharide, hyaluronic
B. Heteropolysaccharides
acid, has both commerical and biological importance. This
The diversity of heteropolysaccharides is enormous. Dis- molecule, a repeating structure of D-glucuronic acid and
tributed throughout the animal and plant kingdom, this N-acetylglucosamine with β-1-3 and β-1-4 linkages, is
class of macromolecules rivals proteins in diversity. Ini- found in bacterial and animal sources, and it is one of the
tially thought to function only as structural components, it few complex saccharides not covalently linked to protein
is now realized that specific sequences may have informa- (Fig. 24). Molecular weights vary depending on source
tion content and can serve as recognition or signaling el- but often exceed two million. The polyanionic nature
ements. In addition, modifications of saccharides already of the molecule leads to a relatively extended solution
incorporated into a polymeric chain (sulfation, for exam- conformation. This coupled with the highly hydrophilic
ple) add an additional level of complexity. The ability of chemistry results in solutions with very high viscosity, an
these materials to function as other than strictly physical importantphysicalproperty.Thisisutilizedintreatmentof