Page 63 - Academic Press Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology 3rd BioChemistry
P. 63
P1: GTQ Final
Encyclopedia of Physical Science and Technology EN006P-81 June 29, 2001 21:48
Glycoconjugates and Carbohydrates 847
O
( 1 3) ( 1 4) ( 1 3) ( 1 3) ( 1 4)
CH 2
O (GlcA GalNAc) n GlcA Gal Gal Xyl Ser
HO H
H C O Chondroitin sulfate
OH H
O CH 2 CH Core protein
H
NH
H NH
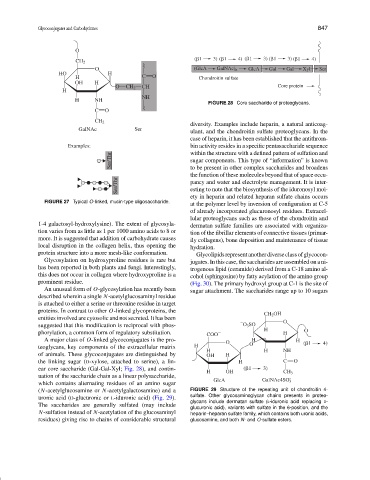
FIGURE 28 Core saccharide of proteoglycans.
C O
CH 2
diversity. Examples include heparin, a natural anticoag-
GalNAc Ser
ulant, and the chondroitin sulfate proteoglycans. In the
case of heparin, it has been established that the antithrom-
Examples: bin activity resides in a specific pentasaccharide sequence
within the structure with a defined pattern of sulfation and
Ser/Thr sugar components. This type of “information” is known
to be present in other complex saccharides and broadens
the function of these molecules beyond that of space occu-
Ser/Thr pancy and water and electrolyte management. It is inter-
esting to note that the biosynthesis of the iduronosyl moi-
ety in heparin and related heparan sulfate chains occurs
FIGURE 27 Typical O-linked, mucin-type oligosaccharide.
at the polymer level by inversion of configuration at C-5
of already incorporated glucuronosyl residues. Extracel-
lular proteoglycans such as those of the chondroitin and
1-4 galactosyl-hydroxylysine). The extent of glycosyla- dermatan sulfate families are associated with organiza-
tion varies from as little as 1 per 1000 amino acids to 8 or tion of the fibrillar elements of connective tissues (primar-
more. It is suggested that addition of carbohydrate causes ily collagens), bone deposition and maintenance of tissue
local disruption in the collagen helix, thus opening the hydration.
protein structure into a more mesh-like conformation. Glycolipidsrepresentanotherdiverseclassofglycocon-
Glycosylation on hydroxyproline residues is rare but jugates. In this case, the saccharides are assembled on a ni-
has been reported in both plants and fungi. Interestingly, trogenous lipid (ceramide) derived from a C-18 amino al-
this does not occur in collagen where hydroxyproline is a cohol (sphingosine) by fatty acylation of the amino group
prominent residue. (Fig. 30). The primary hydroxyl group at C-1 is the site of
An unusual form of O-glycosylation has recently been sugar attachment. The saccharides range up to 10 sugars
described wherein a single N-acetylglucosaminyl residue
is attached to either a serine or threonine residue in target
proteins. In contrast to other O-linked glycoproteins, the
CH 2 OH
entities involved are cytosolic and not secreted. It has been
O
suggested that this modification is reciprocal with phos- O 3 SO
H O
phorylation, a common form of regulatory substitution. COO H
A major class of O-linked glycoconjugates is the pro- O H H ( 1 4)
teoglycans, key components of the extracellular matrix H O
H H NH
of animals. These glycoconjugates are distinguished by OH H
the linking sugar (D-xylose, attached to serine), a lin- H C O
ear core saccharide (Gal-Gal-Xyl; Fig. 28), and contin- ( 1 3)
H OH CH 3
uation of the saccharide chain as a linear polysaccharide,
GlcA GalNAc4SO 3
which contains alternating residues of an amino sugar
(N-acetylglucosamine or N-acetylgalactosamine) and a FIGURE 29 Structure of the repeating unit of chondroitin 4-
uronic acid (D-glucuronic or L-iduronic acid) (Fig. 29). sulfate. Other glycosaminoglycan chains presents in proteo-
glycans include dermatan sulfate (L-iduronic acid replacing D-
The saccharides are generally sulfated (may include
glucuronic acid), variants with sulfate in the 6-position, and the
N-sulfation instead of N-acetylation of the glucosaminyl heparin–heparan sulfate family, which contains both uronic acids,
residues) giving rise to chains of considerable structural glucosamine, and both N- and O-sulfate esters.